OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
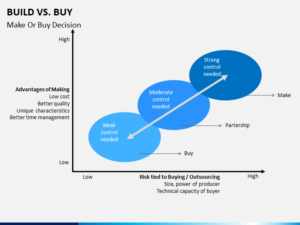
MAKE OR BUY DECISIONS
- Make or Buy Decisions is the determination whether to produce component internally or to buy it from the outside supplier.
- The decision is based on the cost.
- The cost for both the alternatives should be calculated and the alternative with less cost is to be chosen.
CRITERIA FOR MAKE:
- The product can be made cheaper by the firm.
- The finished product is being manufactured only by limited firms.
- The part needs extremely close quality control.
- The part can be manufactured from the existing facilities with experienced operators.
- The quantities are too small and/or no supplier is interested or available in providing the goods.
- Quality requirements may be so exacting or so unusual as to require special processing methods that suppliers cannot be expected to provide.
- There is greater assurance of supply.
- It is necessary to preserve technological secrets.
- It helps the organization obtain a lower cost as the purchase option is too expensive.
- It allows the organization to take advantage of or avoid idle equipment and/or labor.
- It ensures steady running of the corporation’s own facilities, leaving suppliers to bear the burden of fluctuations in demand.
- It avoids sole-source dependency.
- Competitive, political, social or environmental reasons may force an organization to make even when it might have preferred to buy.
- The distance from the closest available supplier is too great. • A significant customer required it.
- Future market potential for the product or service is expanding rapidly and forecasts show future shortages in the market or rising prices.
CRITERIA FOR BUY:
- High investments required for making.
- Does not have facilities for making.
- Skilled workers not available.
- Demand is either temporary or seasonal.
- Patent or legal formalities prevent from making the product.
- The organization may lack managerial or technical expertise in the production of the items or services in question.
- The organization lacks production capacity.
- Certain suppliers have built such a reputation for themselves that they have been able to build a real preference for their component as part of the finished product.
- The challenges of maintaining long-term technological and economic viability for a non core activity are too great.
- A decision to make, once made, is often difficult to reverse.
- It assures cost accuracy.
- There are more options in potential sources and substitute items.
- There may not be sufficient volume to justify in-house production.
- Future forecasts show great demand or technological uncertainty and the firm is unable or unwilling to undertake the risk of manufacture.
- A highly capable supplier is available nearby.
- The organization desires to stay lean.
- Buying outside may open up markets for the firm’s products or services.
- It provides the organization with the ability to b ring a product or service to market faster.
- A significant customer may demand it.
- It encourages superior supply management expertise.
CONSIDERATIONS WHICH FAVOR MAKING:
- Cost considerations (less expensive to make the part).
- Desire to integrate plant operations.
- Productive use of excess plant capacity to help absorb fixed overhead.
- Need to exert direct control over production and/or quality.
- Design secrecy required.
- Unreliable suppliers.
- Desire to maintain a stable work force (in periods of declining sales).
CONSIDERATIONS WHICH FAVOR BUYING:
- Limited production facilities.
- Cost considerations (less expensive to buy the part).
- Small volume requirements.
- Suppliers’ research and specialized know-how.
- Desire to maintain a stable work force (in periods of rising sales).
- Desire to maintain a multiple source policy.
- Indirect managerial control considerations.
- Procurement and inventory considerations.
RELATED VIDEOS FOR MAKE OR BUY DECISIONS:
https://www.myaccountingcourse.com/accounting-dictionary/make-or-buy-decision
