OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
PLANT LAYOUTS
- Layout refers to the arrangement of facilities in a particular workstation. It may be plant layout, office layout, auditorium layout etc.
- Plant Layouts implies the physical arrangement of machines, equipment and other industrial facilities on the factory floor in such a manner that they may be handled efficiently.
- Plant layouts refers to the arrangement of physical facilities such as machinery, equipment, furniture etc. with in the factory building in such a manner so as to have quickest flow of material at the lowest cost and with the least amount of handling in processing the product from the receipt of material to the shipment of the finished product.
- Layout is a Fundamental of every organization and enterprise.
- Kitchen, Retailers, offices, service organization and all the enterprises have a specific layout.
- Previously Layouts were based on intuition, experience and judgment.
- With the complexities and competition now scientific methods are used.
- The Layout comes in picture after the location has been finalized.
- Development of good layout depends on decisions already taken on location, capacity, facility, manufacturing method and material handling techniques.
TYPES OF PLANT LAYOUTS:
There are four broad categories of plant layout:
- Product Layout
- Process Layout
- Fixed Layout
- Group Layout
PRODUCT LAYOUT:
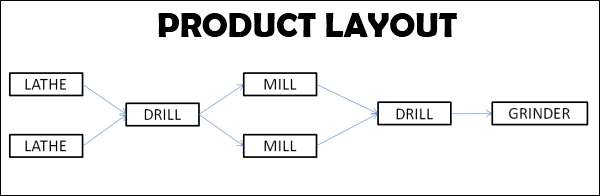
- In product layout, machines and equipment’s are arranged in the sequence of the manufacturing operations required for the product.
- The material is moved from one work station to another sequentially without backtracking or deviation.
- It is also known as Line Layout because machines are mostly arranged in a straight line. The raw materials are fed at one end and taken out as the finished product on the other.
- Output of one machine becomes input to next machine.
- It is a grouping of machines in one sequence. A product layout may assume a straight line shape or U-shape or circular shape.
- Examples: Sugar refineries, Paper mills, Cement plants, Rolling mills, Automobile assembly plants, Food processing chains.
ADVANTAGES:
- Low cost of material handling due to straight and short path and elimination of backtracking.
- Smooth and uninterrupted operations from free bottlenecks.
- Continuous flow of work permits mechanized handling of materials.
- Lesser investment in inventory and work in progress.
- Special purpose equipment can be operated by semi skilled labor.
- Optimum use of floor space and less congestion of work in the process.
- Shorter processing time.
- Simple and effective inspection of work and simplified production control.
- Lower cost of manufacturing per unit.
DISADVANTAGES:
- High initial capital investment in special purpose machines.
- Heavy overhead charges.
- Breakdown of one machine results in work stoppage of the entire line of machines.
- Less flexibility of operations as layout cannot be adapted to the manufacture if any other type of product.
SUITABILITY:
- Mass production of standardized products.
- Simple and repetitive manufacturing processes.
- Operation time for different processes is more or less equal.
- Reasonably stable demand for product.
- Interchangeability of parts.
- Continuous supply of materials.
PROCESS LAYOUT:
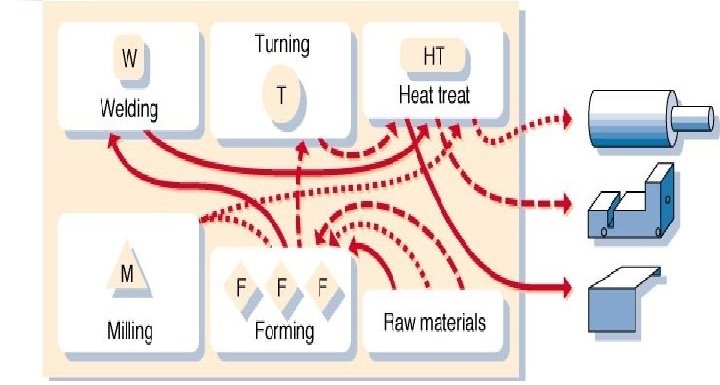
- In process layout, the machines of similar type are located together according to their function.
- Products move between the groups of equipment’s in order of the operations required.
- The work which has to be done, is allocated to the machines according to the loading schedules with the object ensuring that each machine is fully loaded.
- It is used when the operations system must handle a wide variety of products in relatively small volumes.
- It is also known as Functional Layout.
- It is best suited for intermittent type of operation.
- Machines in this layout are general purpose machines.
ADVANTAGES:
- Lower initial capital investment is required in machines and equipment. There is higher degree of machine utilization as a machine is not tied to a single product.
- Overhead costs are relatively low.
- Change in product design and volume can be more easily adapted to the output of a variety of products.
- Breakdown of one machine does not result in complete work stoppage.
- Supervision can be more effective and specialized.
- There is a greater flexibility and scope for expansion.
- Setup and maintenance costs are low.
DISADVANTAGES:
- Material handling costs are high due to backtracking.
- More skilled labor is required resulting in higher labor cost.
- Processing time or time lag in production is higher.
- Work in process inventory is high requiring greater storage space.
- More frequent inspection is needed resulting in costly supervision.
- Production planning and control become difficult.
SUITABILITY:
- Products are not standardized.
- Quantity produced is small.
- There are frequent changes in design and style of product.
- Job shop type of work is done.
- Machines are very expensive.
FIXED POSITION LAYOUT:
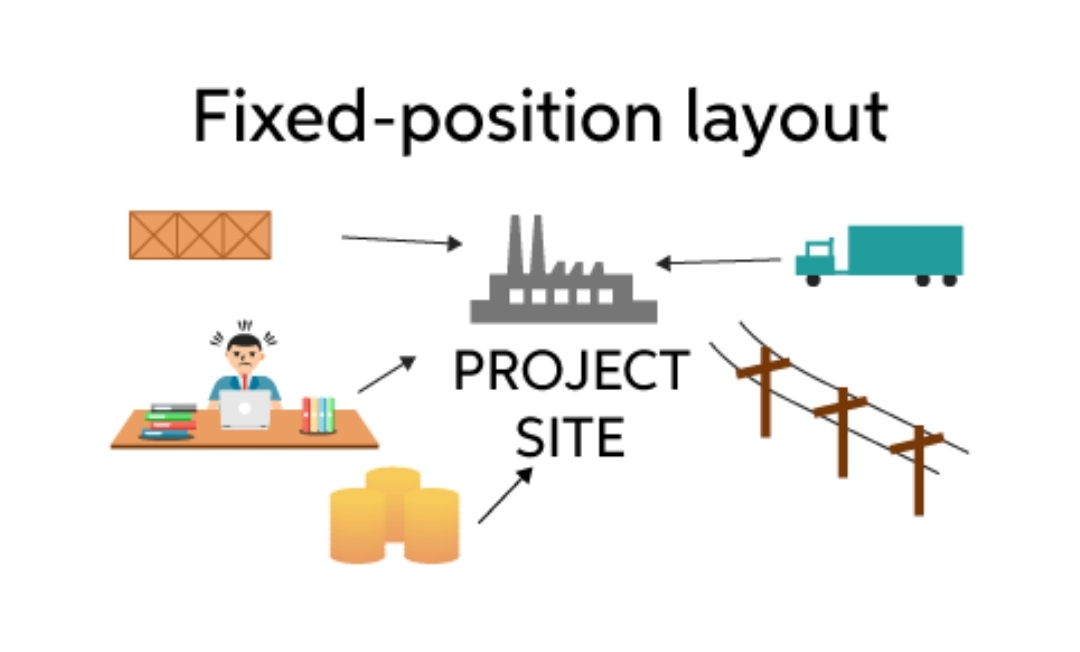
- In fixed position layout, men and equipment are moved to the material, which remains at one place and the product is completed at that place where the material lies.
- This type of layout is used in Ship Building, Aircraft Manufacture, Big Pressure Fabrication etc.
ADVANTAGES:
- It is possible to assign one or more skilled workers for a project from start to finish in order to ensure continuity of work.
- It involves least movement of materials.
- There is a maximum flexibility of all sorts of changes in product and processes.
- A number of quite different projects can be taken with the same layout.
DISADVANTAGES:
- It usually involves a low content of work in progress.
- There appears to be low utilization of labor and equipment.
- It involves high equipment handling costs.
SUITABILITY:
- Manufacture of bulky and heavy products such as locomotives, ships, boilers, generators, wagon building, aircraft manufacturing, etc.
- Construction of building, flyovers, dams.
GROUP LAYOUT:
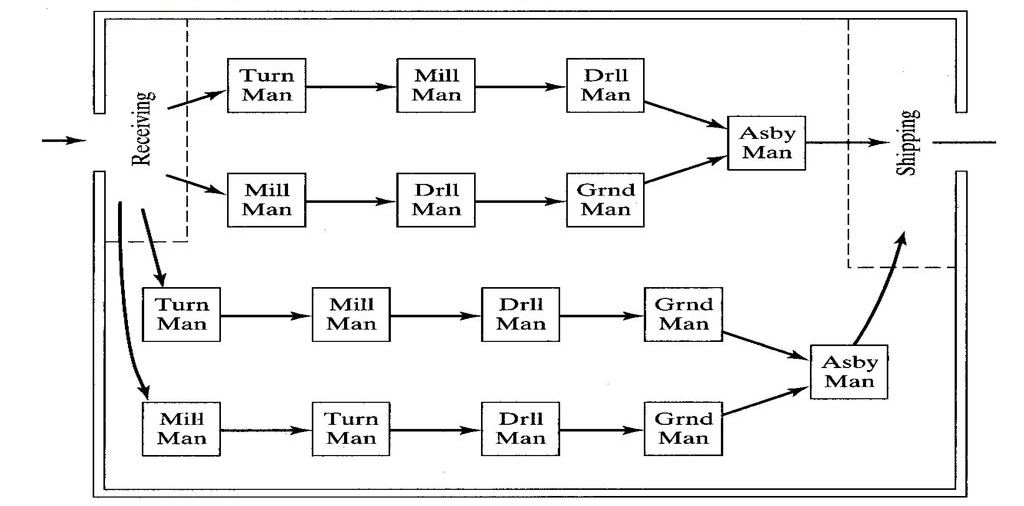
- Group layout is the combination of process and product layouts and it combines the advantages of both types of layout.
- Certain manufacturing units may require all three processes namely intermittent process (job shops), the continuous process (mass production shops) and the representative process combined process.
- In most of industries, only a product layout or process layout or fixed location layout does not exist. Thus, in manufacturing concerns where several products are produced in repeated numbers, Generally, a combination of the product and process layout or other combination are found in practice.
- Industries involving the fabrication of parts and assembly, fabrication tends to employ the process layout, while the assembly areas often employ the product layout.
- In soap, manufacturing plant, the machinery manufacturing soap is arranged on the product line principle, but ancillary services such as heating, the manufacturing of glycerin, the power house, the water treatment plant etc. are arranged on a functional basis.
RELATED VIDEOS FOR TYPES OF PLANT LAYOUTS:
