EXPERIMENT
OBJECTIVE:
To determine the stiffness of the spring and modulus of rigidity of the spring wire.
APPARATUS REQUIRED:
- Spring testing machine.
- A spring.
- Vernier caliper,
- Scale.
- Micrometer.
THEORY:
Springs are elastic member which distort under load and regain their original shape when load is removed. They are used in railway carriages, motor cars, scooters, motorcycles, rickshaws, Governors etc.
According to their uses the springs perform the following functions:
- To absorb shock or impact loading as in carriage springs.
- To store energy as in clock springs.
- To apply forces to and to control motions as in brakes and clutches.
- To measure forces as in spring balances.
- To change the variations characteristic of a member as in flexible mounting of motors.

The spring is usually made of either high carbon steel (0.7 to 1.0%) or medium carbon alloy steels. Phosphor bronze, brass, 18/8 stainless steel and Monel and other metal alloys are used for Corrosion resistance spring. Several types of spring are available for different application. Springs may be classified as helical springs, leaf springs and flat spring depending upon their shape. They are fabricated of high shear strength materials such as high carbon alloy steels spring form elements of not only mechanical system but also structural system. In several cases it is essential to idealize complex structural systems by suitable spring.
PROCEDURE FOR SPRING TESTING:
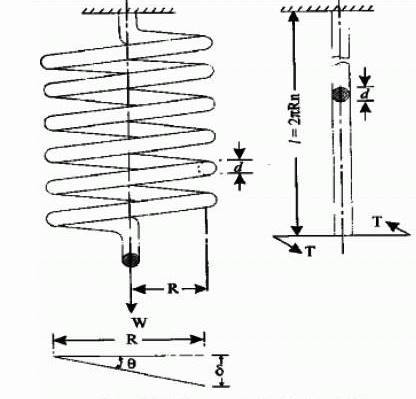
- Measure the diameter of the wire of the spring by using the micrometer.
- Measure the diameter of spring coils by using the vernier caliper.
- Count the number of turns.
- Insert the spring in the spring testing machine and load the spring by a suitable weight and note the corresponding axial deflection in tension or compression.
- Increase the load and take the corresponding axial deflection readings.
- Plot a curve between load and deflection. The shape of the curve gives the stiffness of the spring.
OBSERVATIONS:
- Least count of micrometer = ……… mm
- Diameter of the spring wire, d =……… mm (Mean of three readings)
- Least count of vernier caliper = ……… mm
- Diameter of the spring coil, D = ……… mm (Mean of three readings)
- Mean coil diameter, Dm = D – d =……… mm
- Number of turns, n =………
OBSERVATION TABLE:
|
S. No. |
Load, W (N) |
Deflection, 𝛿
(mm) |
Stiffness, k ([frac up=”N” down=”mm”]) |
Modulus of Rigidity, C |
PRECAUTIONS FOR SPRING TESTING:
- The dimension of spring was measured accurately.
- Deflection obtained in spring was measured accurately.
- Take readings carefully.
ADVANTAGES:
- To apply forces and to control motions as in brakes and clutches.
- To store energy as in clock springs.
- This test is conducted to find the material properties of the spring like modulus of rigidity. This can be obtained by observing the values of deflections of the spring with the application of Different amounts of the load applied along the axis of the spring. The observed Values of deflections are compared with the theoretical value for the deflection of the spring under the load and shear modulus is to be obtained.
- To reduce the effect of shock or impact loading as in carriage springs.
RESULT FOR SPRING TESTING:
The value of spring constant k of closely coiled helical spring is found to be__________ N/ mm.
APPLICATIONS:
- To apply forces and controlling motion, as in brakes and clutches.
- Used in suspension system.
RELATED VIDEOS FOR SPRING TESTING: