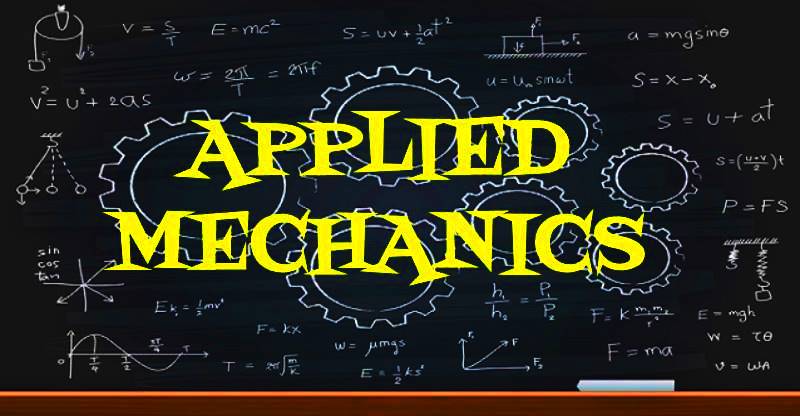
FRICTION:
When two bodies are in contact and have the tendency to move over one another, then resistance to the movement is set up. This resistance is called Friction or Force of friction or Frictional force.
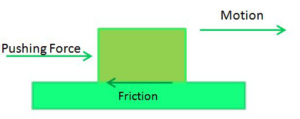
The direction of the frictional force, acting at the point of contact of surfaces, always act in a direction opposite to the direction of the applied force or in which the contact surfaces tend to move. The Frictional force depends upon the nature of surfaces in contact and always acts parallel to the surface of contact.
IMPORTANCE OF FRICTION IN PRACTICAL APPLICATIONS:
- There are a number of applications where friction is desirable and efforts are made to maximize it. For example: Belts, Ropes, Brakes, Clutches etc.
- There are number of applications where Frictional force is undesirable and it result into loss of power, thus efforts are made to minimize it by lubrication.
Thus, Frictional force is both desirable and undesirable. We would have not been able to walk, skate and drive automobiles if friction were absent. Hence, Frictional force is said to be a necessary evil in practical applications.
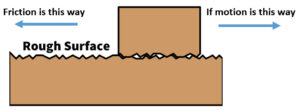
Motion over rough surface
The major cause of Frictional force is believed to be microscopic roughness of the contact surfaces as no surface is perfectly smooth. Every surface is composed of crests and falls. It is the interlocking of the crests of one surface into the falls of the other surface which produces the resistance against the movement of one body over the other body. When the force exerted is sufficient to overcome the Frictional force, the movement ensures and the crests are being sheared off. This gives rise to heat and raises the local temperature. This is also the reason of the wear of the contact surface. This phenomenon of Frictional force necessitates the presence of fluid film between the two surfaces to avoid wear of surfaces. The process of creating the fluid film between the contact surfaces is known as lubrication.

Let us consider a block of Weight ‘W’ kept on a rough horizontal surface and a force F is acting on the block. Due to this force F, the block has the tendency to move in the direction of the force, then a force Ff which opposes the motion, known as Frictional force, will act at the contact surfaces of the block and horizontal surface.
The forces acting on the block are
F = Applied force
W= Weight of the block
FN = Normal reaction acting on the block due to the surface
Ff = Frictional force
If the force F is so small that it can just move the body then
F = Ff
FN = W
TYPES OF FRICTION:
Friction can be classified into two types
(a) Static Friction (b) Dynamic Friction
(a) STATIC FRICTION:
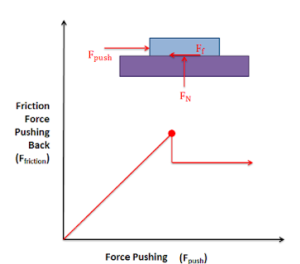
It comes into play before the body tends to move on the surface. Its magnitude is equal to the applied force. It varies from zero to maximum till the movement ensures.
(b) DYNAMIC FRICTION:
It comes into play when a body is in motion over the another body or motion of the body over the other. It is also known as Kinetic friction. Its magnitude is constant.
It is further divided into the following two types:
(i) Sliding Friction (ii) Rolling Friction
(i) SLIDING FRICTION:
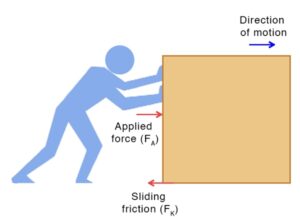
It is experienced by a body when it slides over another body.
Example: When a piston slides in the cylinder of the engine.
(ii) ROLLING FRICTION:
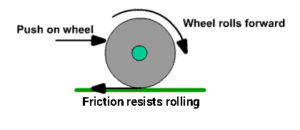
It is experienced by a body when it rolls over another body.
Example: When the car moves on the road.
RELATED VIDEOS: