CONVENTIONAL REPRESENTATION
Certain draughting conventions are used to represent materials in section and machine elements in engineering drawings.
Conventional representation refers to standardized symbols, notations, and simplified depictions used in technical drawings, blueprints, and schematics. These representations help engineers, architects, and manufacturers communicate design intent clearly without excessive detailing.
MATERIALS:
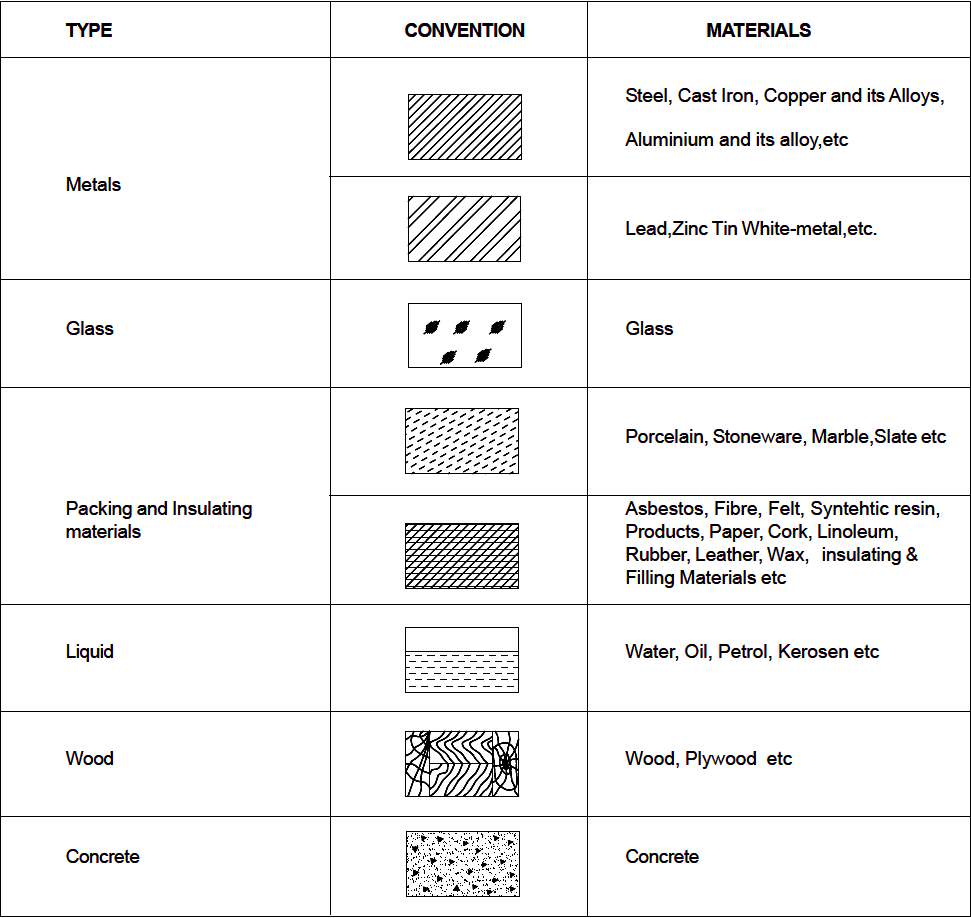
As a variety of materials are used for machine components in engineering applications, it is preferable to have different conventions of section lining to differentiate between various materials.
CONVENTIONAL SECTIONS FOR MATERIALS :
Conventional sections for materials are standardized methods used in engineering and manufacturing to represent the internal structure, composition, and features of a material or component. These sections are crucial for understanding the material’s properties, ensuring quality control, and facilitating communication between designers, engineers, and manufacturers.
Cross-Sectional View
- Purpose: To reveal the internal structure of a material or component by cutting it perpendicular to its axis.
- Applications: Used in metallurgy, composites, and structural engineering to analyze grain structure, porosity, layering, or internal defects.
- Types:
- Transverse Section: Cut perpendicular to the longitudinal axis (e.g., analyzing the cross-section of a cylindrical rod).
- Longitudinal Section: Cut parallel to the longitudinal axis (e.g., examining layers in a laminated material).
- Representation: Shown in technical drawings with hatching or shading to differentiate materials.
RELATED VIDEOS FOR CONVENTIONS: