SCREW THREADS
Different parts of structures, machines or other parts are joined together by means of fasteners. The fasteners used for this purpose are for temporary fastening i.e. the parts can be separated easily without breaking just by unscrewing or removing the fastener. The fastener used for this purpose are keys, cotters, pins, studs, nuts and bolts etc. The screw thread(s) is the functional element of temporary fastening which is used on a bolt, stud, set screw, cap screw, wood screw etc. Screw threads are formed by cutting a helical groove on a circular either inside or outside surface. The threaded surface of a part is call a screw.
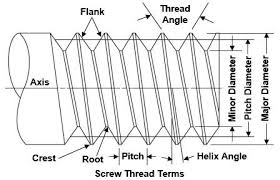
- PITCH: It is the distance from top of one thread to the top of the adjacent thread along the axis of the rod.
- ROOT: It is the surface of a thread which connects adjacent flanks at the bottom of the groove.
- FLANK: The flanks are the parts of the surface between root and crest. These are inclined lines starting from crest towards roots forming a solid surface with inclined side surfaces.
- CREST: It is the part of the surface of the thread which connects adjacent flanks at the top of ridge.
- LEAD: It is the distance moved by a nut or bolt in the axial direction in one complete revolutions. In single start threads, the lead is equal to the pitch. In multi start threads, lead is equal to the number of starts multiplied by pitch.
- ANGLE OF THREAD: It is the angle between the flanks measured in an axial plane.
- MAJOR DIAMETER: The diameter of the imaginary cylinder at crest or on which threads are cut is known as major diameter.
- MINOR DIAMETER: The diameter of the imaginary cylinder at root is known as minor diameter.
- PITCH DIAMETER: The mean of major and minor diameter is known as pitch diameter.
- EXTERNAL THREAD: A thread on the outside surface of a member such as bolt, stud, screw, pipe, cylinder, shaft etc.
- INTERNAL THREAD: A thread on the inside surface of a member such as threads in the hole of the nut, pipe, cylinder etc.
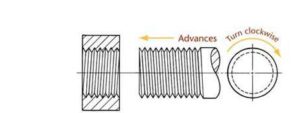
- RIGHT HAND THREAD: The thread on the outer surface of bolt rod which advanced into the nut when turned in a clockwise direction or in which thread slopes up towards the left when screw is placed horizontally.
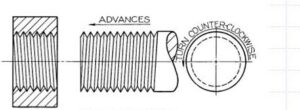
- LEFT HAND THREAD: The thread on the outer surface of bolt rod which advanced into the nut when turned in an anticlockwise direction or in which the direction of the thread slopes up towards the right when screw is placed horizontally.
- SINGLE START THREAD: In a single start thread, the pitch is equal to the lead, when only one helix or one starting point is seen forming the thread, run on a cylinder throughout its length. If a nut is screwed on the threaded bolt and held firmly at one point, the rod is rotated by 360°, the nut slides along the axis equal to pitch of the thread.
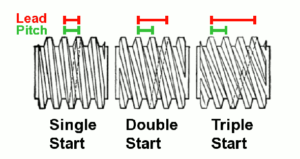
- DOUBLE START THREAD: In double start thread, the threads in the inner surface of the hole of nut should also be double start thread. If a nut is screwed on the double start threaded bolt or rod and the rod is rotated by 360°, the nut will lead or shift twice the pitch of the thread.
- MULTI-START THREAD: In multiple start threads, two or more threads having the same pitch run parallel to one another.
Multiple start threads are used wherever, quick motion in minimum rotations is required and application of great force is not allowed such as between fountain pen and its cap, bottles, toothpaste caps, valves, water tap spindles etc. to impart quick movement in opening an closing.
FORMS OF SCREW THREADS:
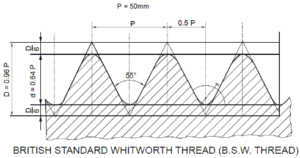
- B.S.W. (British Standard Whitworth):
BSW thread is used as a standard thread in British for general purposes. It is the modified form of V thread with angle of threads 55° and corners equally rounded off at crest and root for smooth movement of threads. This type of thread is used on bolts, nuts and other screwed fastenings.
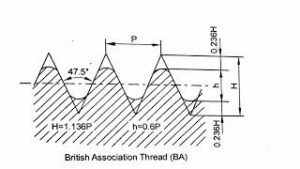
- B.A. (British Association) Thread Section:
BA thread is recommended by British standard and institute for use in preference to BSW thread for all small screws and small instruments works. The angle between flank is 47.5°. It is used where accuracy is main consideration such as i aircrafts an mathematical instruments.
- Seller Thread Section or American National Thread Section:
This thread is used as a standard thread in America for general purposes. The angle between two flanks of the thread is 60º. It is used on bolts, nuts, machine screws etc.
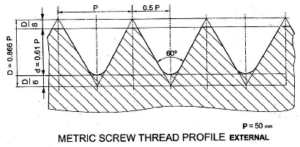
- Metric Thread:
This thread is used as a standard thread in India for general purposes. The metric thread is a symmetrical V thread with an angle of 60º between flanks. The thread on the bolt is rounded off at the root and flat at the crest and the thread on the nut is rounded off at the root but the crest is flat.
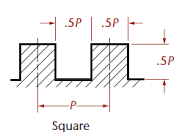
- Square Thread Section:
This thread is of square shape and it is used for power transmission. The depth and thickness are equal to half the pitch. It is used in screw jack, vice screws, large valve spindles because they it offer least frictional resistance to motion.
- Knuckle Thread Section:
Knuckle threads are generally used in some type of electric bulbs, bottle tops, fire hydrant and railway couples etc. It is the modified form of square thread. It is semi circular shaped thread. It is not easily damaged when subjected to rough usage.
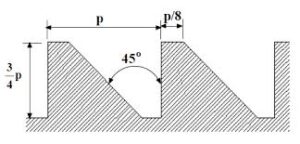
- Buttress Thread:
In the buttress thread section, one side of the thread is perpendicular to axis whereas the other side is kept at 45º inclined to axis. The buttress threads are used for the transmission of power in one direction only such as in spindles of bench vices, propellers etc.

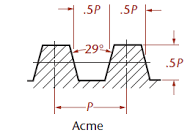
- Acme Thread Section:
It is the modification of square thread. The shape of the thread can be cut very easily which gives more strength to the threads because of its broader base and narrow top. The angle between thread flanks is 29º.
RELATED VIDEOS FOR SCREW THREADS:
For More Information- CLICK HERE