STUDS:
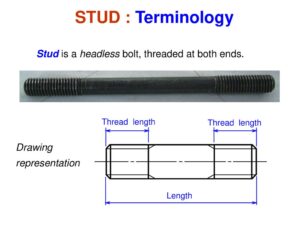
A stud is just like a bolt but has no head. Both of its ends are threaded leaving a small portion at the center. The stud is screwed tightly into the threaded hole in the part until it jams. The collar is sometimes provided in the center and in some case, the central portion is made square to receive spanner for tightening purposes. Theses studs when screwed to the part become assembled and the other part which is drilled is easily placed in position. A nut screwed on other end of the stud holds the two part together. These are used to fit end covers.
MACHINE SCREWS:
A machine screw is a small threaded circular rod with threading on one side and having a head on one side to function as a small fastener. It is used with a nut to function in the same manner as a bolt or without a nut to function as a cap screw. It passes through a clearance hole in one part and is screwed into tapped hole in the other part, thus assembling the two parts. The head of a machine screw is provided with a slot for screwing or unscrewing by a screwdriver. The machine screws are extensively used in jigs, fixtures, dies, firearms etc.
SET SCREWS:
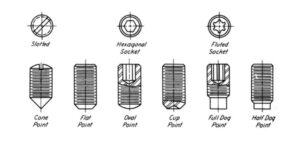
A set screw is threaded throughout its length, and is generally used to prevent relative movement between two parts. Basically, it serves the same purpose that a key serves. It is screwed into a tapped hole and its point end passes on the other par, thus preventing their relative rotation and sliding movement. These are made of hardened steel. The head types of set screws are operated by spanner. The headless types of set screws are known as grub screws and are used where the surface of the machine part is required to be free. Headless set screws are provided with a slot for screw driver or hexagonal hole for special type of hexagonal; steel bar bent at right angles, known as allen key or screwing on and off. Set off screws are used in fast and loose pulleys, connecting rod ends etc.
NUT LOCKING (LOCKING DEVICES):
- LOCK NUT: It is one of the locking devices in which two nuts one small and the other having standard thickness are given. Both nuts are chambered from both sides. The lower or small nut is known as lock nut. The lock nut is first tightened down upon the bolt, then the upper main nut is tightened down upon it.
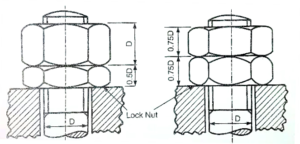
Lock Nut
- SPRING WASHER: It is one of the locking devices in which tightening of nut on spring washer results in exerting upward pressure on the nut in thrusting the nut threads against the bolt threads thus increasing the friction between them.
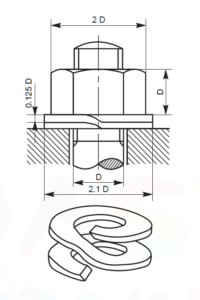
Spring Washer
- SPLIT PIN LOCKING: It is one of the locking devices in which a hole is drilled through the stem of the bolt and a split pin is driven through the hole after fully tightening the nut. The legs of the split pin are bent outward to prevent nut becoming loose.
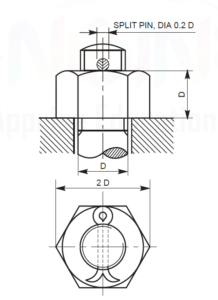
Split Pin
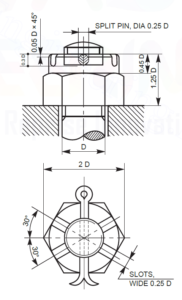
- SLOTTED NUT: It is the locking device in which the slots are cut in the upper surface and opposite faces. A circular hole is also made in the threaded end of the bolt. When the nut is screwed on bolt and tightened, one of the slots come in line with the hole. A split pin is inserted through the slot and the hole and it is bent out as its ends. The pin keeps the nut in position. Slotted nuts are used on the parts which are subjected to shock and vibrations.
Slotted Nut
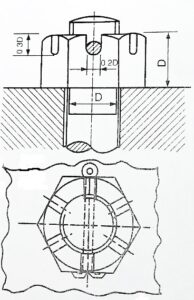
- CASTLE NUT: Instead of making slots on the nut, it has cylindrical collar on its upper surface. The slots are made on the collar with the center of each face. The split pin passes through slot and the hole and it is bent outward. There is no reduction in strength of the nut due to additional collar. It is used for locking the wheels of automobiles and vibrating engine parts.
Castle Nut
- LOCKING PLATE: It is one of the locking devices in which the grooves in the plate are cut in such a way that the hexagonal nut fits in it any position turning through 30 degree. There is another hole in the plate for fixing it with adjoining piece around the nut by means of machine screw. The locking plate when in position prevents the rotation of the nut.
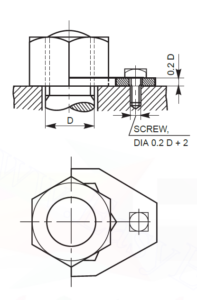
Locking Plate
- SAWN NUT: It is an ordinary hexagonal nut having a saw cut half way across it. Upper part of the cut position has a clearance hole and the lower part a tapped hole. When the nut is screwed in position and tightened, a set screw is passed through the clearance hole and tightened in the tapped hole. When the screw is tightened, the upper part slightly bend downward resulting in increasing the friction between the bolt and threads in the nut. The friction prevents the nut from slackening. For small nuts, when there is no space for screw, the upper part is slightly bend down by a hammer blow.
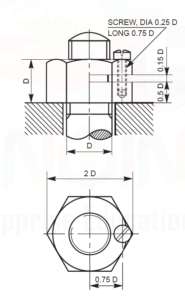
Sawn Nut
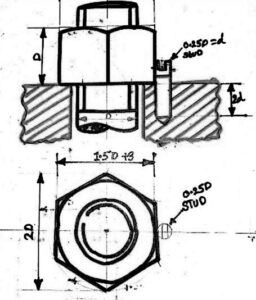
- STUD LOCKING: A tapped hole is drilled in the adjoining piece around the nut. After the nut is tightened, the stud is screwed into the hole. The spacing between the stud and nut is kept in a way that the stud should touch flat surface of the nut.
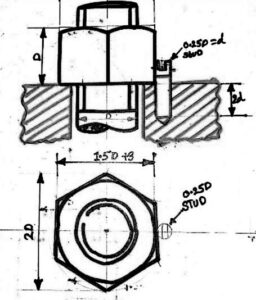
Stud Locking
- RING COLLAR NUT: The bolt hole required counter boring to receive the cylindrical portion of the nut. The grooved cylindrical collar is integral part of hexagonal nut which receives the tip of the set screw. It will prevent the nut form getting loose. It is used on marine engines.
Ring Collar Nut
- TAB WASHER: It is often used under the nut at the end of the part. A hexagonal nut fits in any position at intervals of 60 degrees. After tightening the nut, two edges of the plate are turned up and down respectively against a flat surface on the nut.
Tab Washer
REALTED VIDEOS FOR STUDS AND LOCKING DEVICES: