SCREW FASTENERS:
Fasteners are used to join two or more parts together temporarily so that the parts assembled can be dissembled and assembled easily. Studs, Nuts and Bolts are the few examples of the fasteners.
BOLTS:
The bolt is a straight rod having an integral head on one side and threaded on the other end. It is passed through clearance holes in two or more aligned parts together. A nut is screwed on the threaded end of the bolt to tighten the parts together. A bolt and nut form one screw fastener as a unit.
HEXAGONAL HEADED BOLT:
The bolt with a hexagonal head on one side and threaded on the other end is called bolt. The bolt may be threaded throughout its length or partly threaded.

Ratio and proportions of hexagonal headed bolt:-
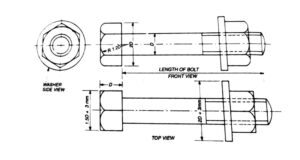
Width across flats, W = 1.5 D + 3 mm
Thickness of head, T = 0.8 D
Angle of chamfer = 30° to the base of head
Radius of chamfer, R = 1.4 D
Length of threaded portion, L1 = 2D + 5 mm up to 80 mm diameter
or L1 = 2D + 10 mm from 81 to 200 mm diameter
or L1 = 2D + 20 mm above 200 mm diameter.
SQUARE HEADED BOLT:
It is another common form of bolt. The contact area of the head with the part to be tightened is comparatively small as compared to hexagonal nut. It is generally used where the head of the bolt is to accommodated in a recess which is itself of square form. The head rests in the square recess with little clearance. When the nut is tightened or screwed off, the square recess prevents the head from turning.

Ratio and proportions of square headed bolt:-
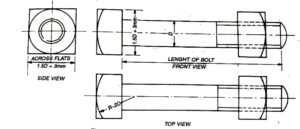
Width across flats, W = 1.5 D + 3 mm
Thickness of head, T = D
Angle of chamfer = 30° to the base of head
Radius of chamfer, R = 2 D
Length of threaded portion, L1 = 2D + 5 mm up to 80 mm diameter
or L1 = 2D + 10 mm from 81 to 200 mm diameter
or L1 = 2D + 20 mm above 200 mm diameter.
RELATED VIDEOS FOR TYPES OF BOLTS: