GEOGRAPHY
Classification of Geography:
- Physical
- Geomorphology
- Climatology
- Oceanography
- India
- Physical
- Human/Economic
- World
- Asia
- Europe
- America
- Africa
Meaning and span of Geography
Geo means Earth and Grapho means Study. Thus, Geography means study of Earth.
Geography can be divided into two parts:
- Physical Geography
- Human Geography
Fundamentals of Geography:
- Latitudes
- Longitudes
- Seasons on Earth
- Time-zones
LATITUDES:
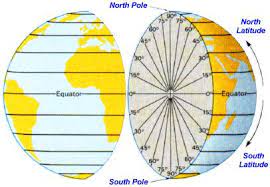
- Latitudes are the imaginary lines on the earth.
- Latitudes are angular distance of a plane from the equator.
- All latitudes are concentric circles.
- Latitudes are called parallel as well.
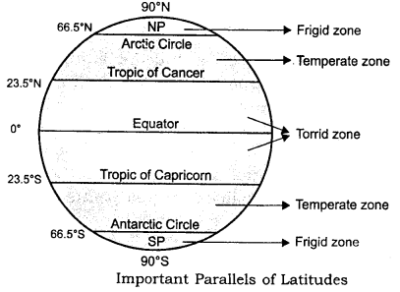
- Torrid zones are heat surplus regions.
- Temperate zones and frigid zones are heat deficient regions.
- Equator is the largest latitude.

Source: edubaba
- The Equator passes through 3 continents: South America, Africa, and Asia.
- The Equator passes through 13 countries: Ecuador, Colombia, Brazil, Sao Tome & Principe, Gabon, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda, Kenya, Somalia, Maldives, Indonesia and Kiribati.
- The Equator passes through 3 Water Bodies: Atlantic Ocean, Pacific Ocean, Indian Ocean.
- There is no Equator going via India. India is north to the equator.
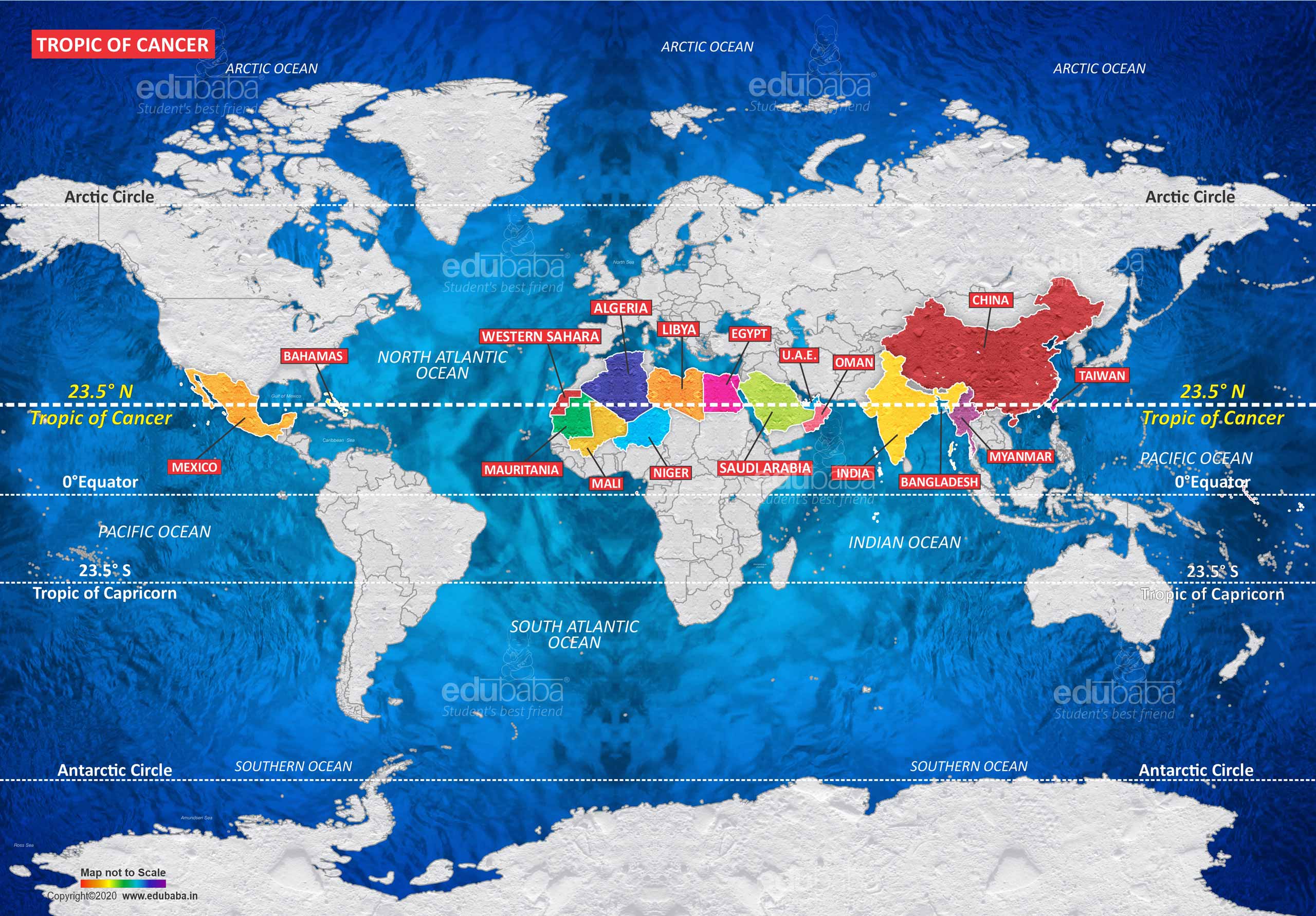
Source: edubaba
- The Tropic of cancer passes through 3 continents: North America, Africa, and Asia.
- The Tropic of cancer passes through 17 countries: Bahamas (Archipelago), Mexico, Egypt, Libya, Niger, Algeria, Mali, Western Sahara, Mauritania, Taiwan, China, Myanmar, Bangladesh, India, Oman, United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia.
- The Tropic of cancer passes through 6 Water Bodies: Indian Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, Pacific Ocean, Taiwan Strait, Red Sea and Gulf of Mexico.
Source: edubaba
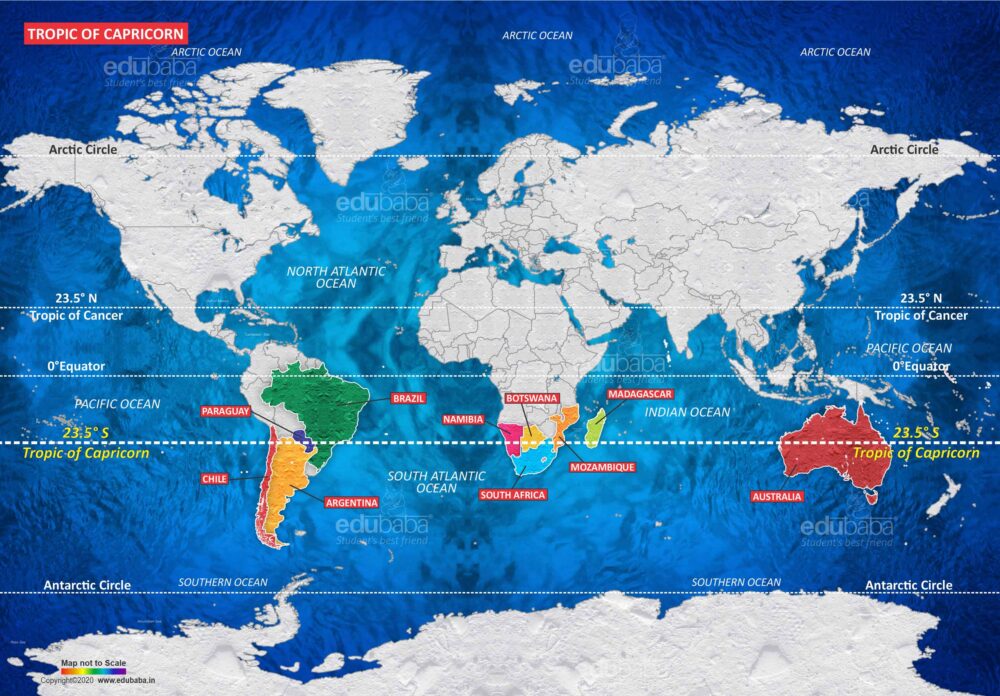
- The Tropic of Capricorn passes through 3 continents: South America, Africa and Australia.
- The Tropic of Capricorn passes through 10 countries: Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Paraguay, Namibia, Botswana, South Africa, Mozambique, Madagascar, and Australia.
- The Tropic of Capricorn passes through these Water Bodies: Indian Ocean, Atlantic Ocean and Pacific Ocean.
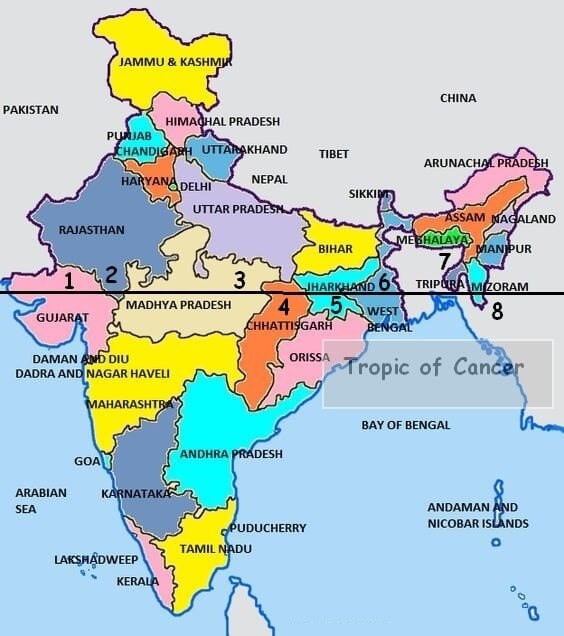
- Tropic of Cancer passes through 8 Indian states (west to east): Gujarat – Rajasthan – Madhya Pradesh – Chhattisgarh – Jharkhand – West Bengal – Tripura – Mizoram.
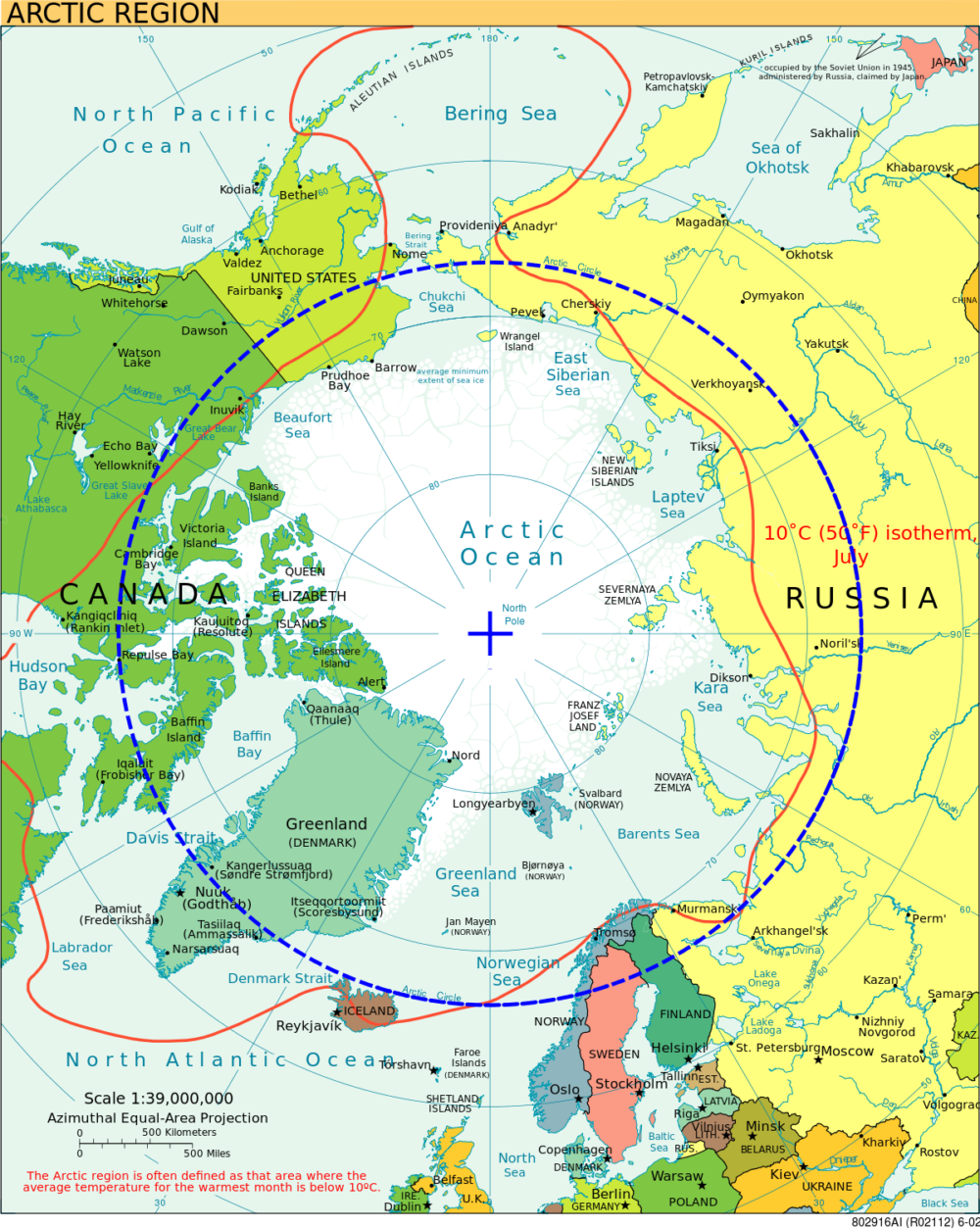
- The Arctic Circle is penetrated by 7 countries: Canada, Finland, Greenland, Norway, Sweden, Russia and Alaska (USA).
HEAT ZONES OF THE EARTH
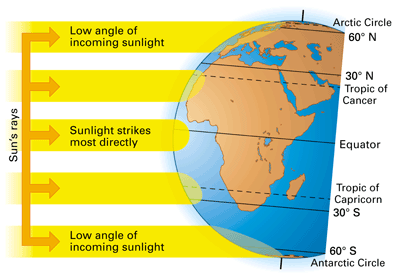
- The mid-day sun is exactly overhead at least once a year on all latitudes in between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. This area, therefore, receives the maximum heat and is called the Torrid Zone.
- The mid-day sun never shines overhead on any latitude beyond the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. The angle of the sun’s rays goes on decreasing towards the poles. As such, the areas bounded by the Tropic of Cancer and the Arctic circle in the northern hemisphere, and the Tropic of Capricorn and the Antarctic circle in the southern hemisphere, have moderate temperatures. These are, therefore, called Temperate Zones.
- Areas lying between the Arctic Circle and the North Pole in the northern hemisphere and the Antarctic Circle and the South Pole in the southern hemisphere, are very cold. It is because here the sun does not rise much above the horizon. Therefore, its rays are always slanting. These are, therefore, called Frigid Zones.
- If the earth were flat that it would receive equal heat in all the zones but the Earth is spherical and due to this sunlight strikes most directly at the equator and torrid zones and makes it heat surplus region. Sunlight does not strikes directly at the temperate zones and frigid zones and due to this reason the sunlight gets dispersed and its heat intensity is reduced thus making the temperate zones and frigid zones a heat deficient region.
- As the earth is spherical so heat reception on Frigid, Temperate and Torrid zones are different thus a pressure difference is created on the earth and due to this pressure difference, wind system is developed on the earth.
SEASONS ON EARTH
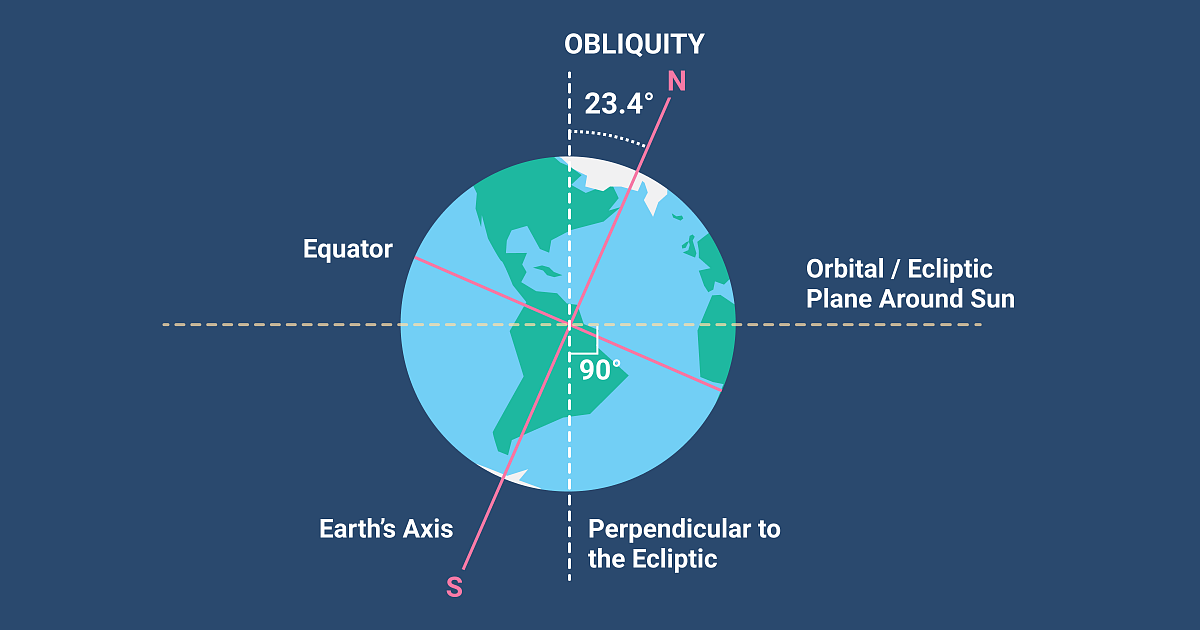
Earth is tilted at 23.5° relative to the orbital plane and due to this reason Earth has seasons.
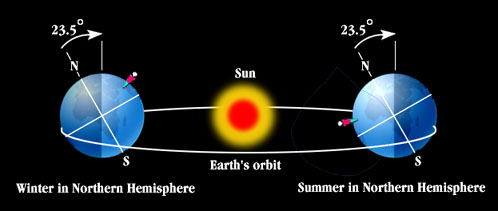
- In case (a), Northern Hemisphere is away from the sun and Southern Hemisphere is tilted towards the sun, due to this Southern Hemisphere receives more heat as compared to the Northern Hemisphere. This is the reason for winter in Northern Hemisphere in case (a).
- In case (b), Northern Hemisphere is tilted towards the sun and Southern Hemisphere is away from the sun, due to this Northern Hemisphere receives more heat as compared to the Southern Hemisphere. This is the reason for summer in Northern Hemisphere in case (b).
SUMMER AND WINTER SOLSTICE
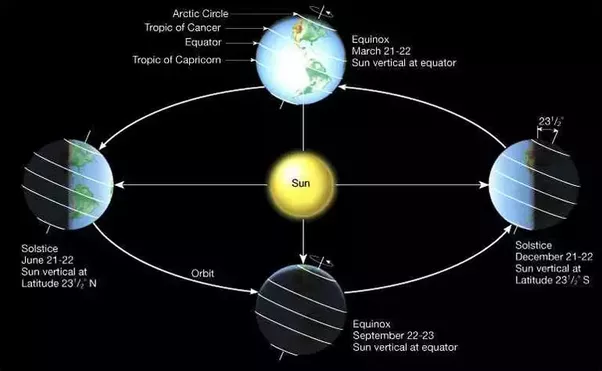
- Earth revolves around the sun in an elliptical path and due to this when the Earth is on the minor axis, it will be closest to the sun and when the earth is on the major axis, it will be farthest from the sun.
- The day that the Earth’s North Pole is tilted closest to the sun is called Summer Solstice. It is the longest day on the earth. It is also the day that sun reaches its highest point in the sky. 21st June – Summer Solstice – Longest day of the summer season.
- The day that the Earth’s North Pole is tilted farthest from the Sun is called Winter Solstice. It is the shortest day of the year. 21st December – Winter Solstice – Shortest day of the winter season.
- In between, when the earth is at the major axis then the tilt of the axis is zero, meaning that the tilt is neither away from the sun nor towards the sun. These are the Vernal Equinox or Spring Equinox – the first day of spring and the Autumnal Equinox – the first day of fall. During these times the hours of daylight and night are equal. Both are 12 hours long.
| Summer Solstice | 21st June | Longest Day Of Summer |
| Winter Solstice | 21st December | Shortest Day Of Winter |
| Vernal Equinox | 20th March | First Day Of Spring |
| Autumnal Equinox | 23rd September | First Day Of Fall |
DAYLIGHT SAVING IN TEMPERATE REGIONS:
- Daylight saving is the practice of turning the clock ahead as warmer weather approaches and back as it becomes colder again. The purpose of doing so is that people will have one more hour of daylight in the afternoon and evening during the warmer season of the year.
- The daylight saving is followed in over 70 countries on various dates.
- India does not follow daylight saving time; countries near the equator do not experience high variations in daytime hours between seasons.
- Initially it was followed by a group of Canadians on July 1st 1908, when residents of Port Arthur, Ontario, turned their clocks forward by an hour. Other locations in Canada soon followed it.
- However, globally Germany and Austria introduced DST on April 30th 1916, the rationale being to minimize the use of artificial lightening to save fuel during World War I.
- A century ago, when DST was introduced, more daylight means less use of artificial light. But modern society uses so many energy consuming appliance all day long that the amount of energy saved is negligible.
- DST disrupts the body clock or Circadian Rhythm.
LONGITUDES:
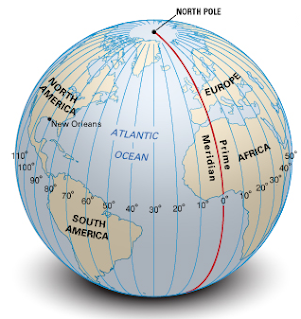
- Longitudes are the angular distance of a place from Prime Meridian.
- They have one very important function; they determine local time in relation to GMT (Greenwich Mean Time) or world time.
- The meridian which passes through Greenwich (UK), where the British Royal Astronomical Observatory is located. This meridian is considered as the PRIME MERIDIAN.
- Its value is 0° longitude and from it we can count 180° eastwards as well as 180° westwards. The prime meridian and 180° meridian divides the earth into two halves, the eastern hemisphere and the western hemisphere.
INTERNATIONAL DATE LINE
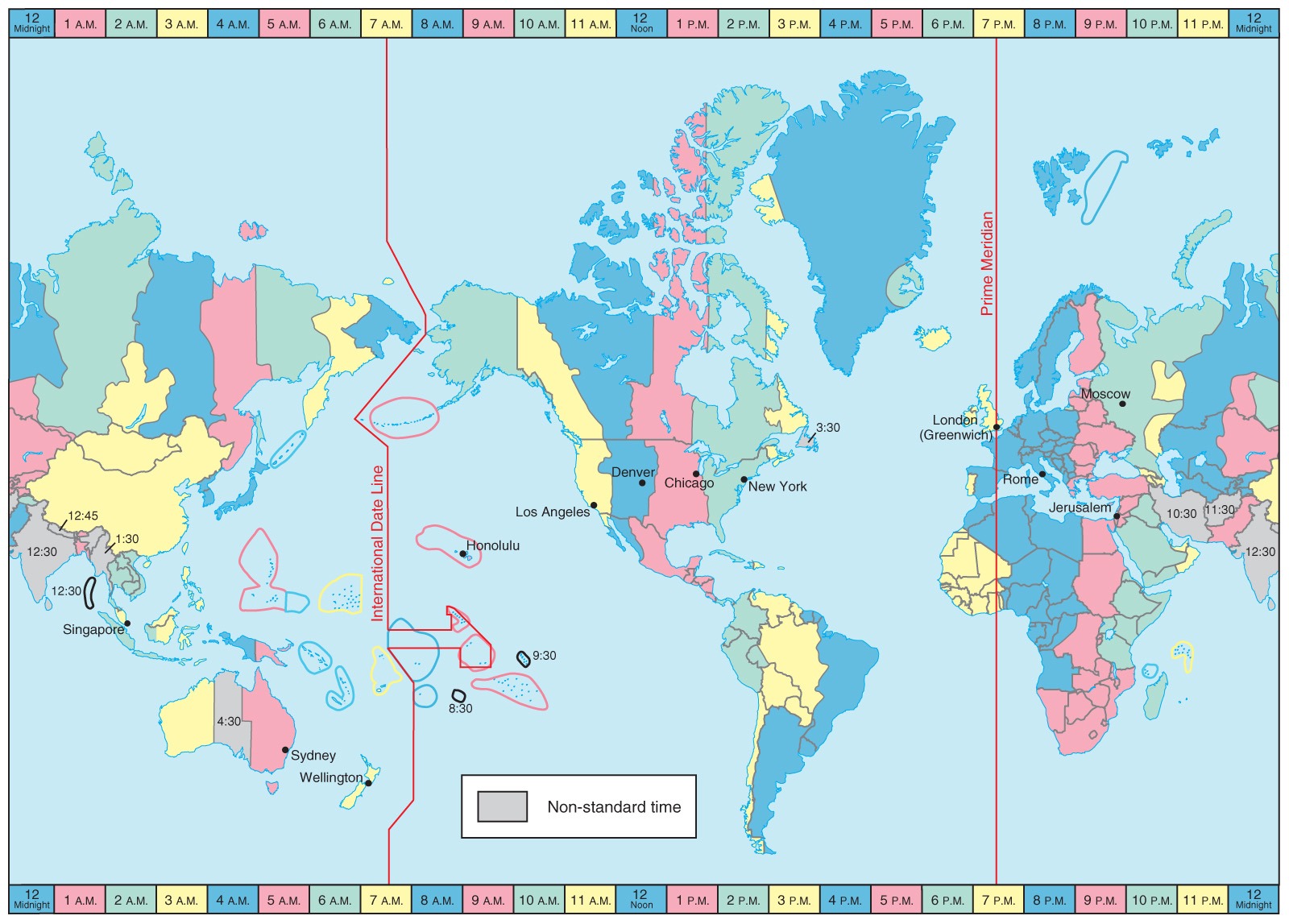
Source: Pearson Prentice Hall
- The International Date Line is in the middle of the time zone defined by 180° meridian.
- At International Date Line where the date changes by exactly one day when it is crossed. A traveler crossing the date line from East to West loses a day and while crosses the dateline from West to East he gains a day.
- The international date line in the mid pacific curves from the normal 180° meridian at the Bering Strait, Fiji, Tonga and other islands to prevent the confusion of day and date in some of the island groups that are cut by the meridian.
- International Date Line passes through the Pacific Ocean and it is an imaginary line like longitudes and latitudes. Some of the islands (Polynesia, Melanesia, Micronesia) fall on either of the date zones. Thus to avoid any confusion of date, this line is drawn through where the sea lies and not land. Hence IDL is drawn in a zigzag manner.
STANDARD TIME
- Since the earth makes one complete revolution of 360° in one day or 24 hours, it passes through 15° in one hour or 1° in 4 minutes.
- The earth rotates from west to east, so every 15° we go eastwards, local time is advanced by 1 hour. Conversely, if we go westwards, local time is retarded by 1 hour.
- If each town were to keep the time of its own meridian, there would be much difference in local time between one town and the other. The traveler going from one end of the country to the other would have to keep changing their watches if they wanted to keep their appointments. This is impractical and inconvenient.
- To avoid all these difficulties, a system of standard time is observed by all the countries. Most countries adopt their standard time from the central meridian of their countries.
- In larger countries (on horizontal scale) such as Canada, USA, China and USSR, it would be inconvenient to have single time zone. So these countries have multiple time zones.
- Canada and USA have 5 time zones.
- Russia has 9 time zones.
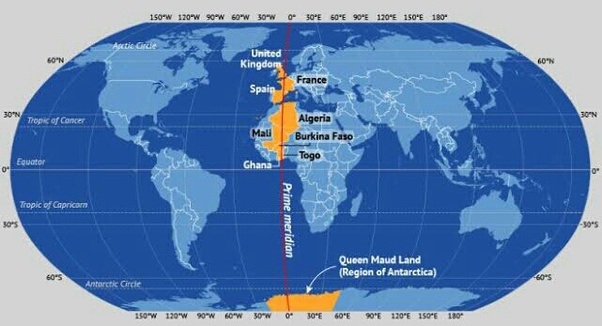
- The Prime Meridian passes through 3 continents: Europe, Africa and Antarctica.
- The Prime Meridian passes through 9 countries: United Kingdom, France, Spain, Algeria, Mali, Burkina Faso, Ghana, Togo and Antarctica.
- The Prime Meridian passes through 6 water bodies: Arctic Ocean, Norwegian Sea, Greenland Sea, Mediterranean Sea, Atlantic Ocean and Southern Ocean.
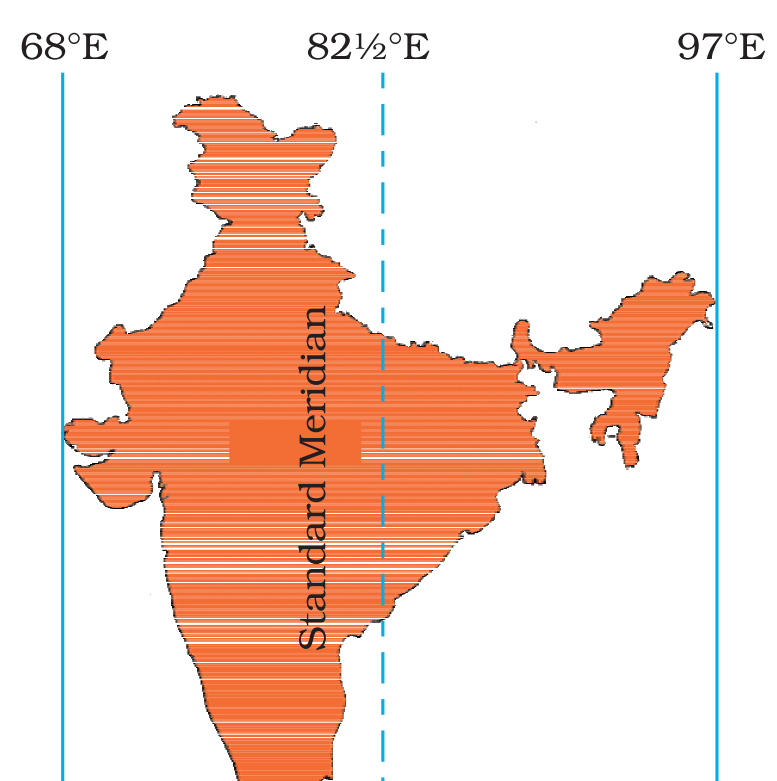
- India lies between 68° E and 97°E meridian.
- Indian government has accepted the meridian of 82.5° E for the standard time which is 5 hours 30 minutes ahead of GMT.
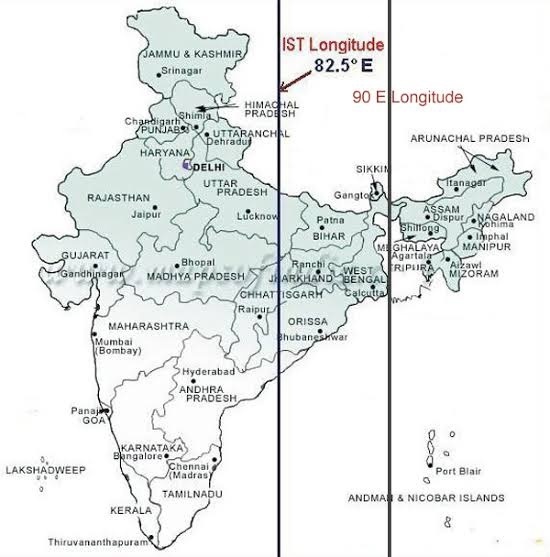
- The standard meridian of India passes through the following 5 states U.P., M.P., Chhatisgarh, Orissa and Andhra Pradesh.
- The Standard Meridian of Indiahas a longitude of 82°30’E. This Standard meridian passes through Mirzapur in Uttar Pradesh and it is considered as the standard time for the whole country.
CHAIBAGAAN TIME:
- 150 years ago British Colonialists introduced Chaibagaan time or Bagaan time in north-east India, a time schedule observed by tea planters which was one hour ahead of IST.
- This was done to improve the productivity by optimizing the usage of daytime (for the convenience of European tea planters).
- After independence, Assam along with the rest of India has been following IST for last 66 years.
- The administration of the Indian state of Assam now wants to change its time zone back to the Chaibagaan time to conserve and improve productivity. But Indian government did not accept such a proposal. (proposal was given by CM Tarun Gogoi in 2014)
DEFINITIONS FROM NCERT
- The sun, moon and all those objects shining in the night sky are called Celestial Bodies.
- Celestial bodies which have their own heat and light, which they emit in large amounts, are called stars. Sun is also a star.
- Different groups of stars are called Constellations. There are 84 constellations.
- 5 major constellations are The Big Dipper/Ursa Major, ‘The Great Bear’, The Little Dipper/Ursa Minor, ‘The Little Bear’, Orion, ‘The Hunter’ , Taurus, ‘The Bull’ and Gemini, ‘The Twins’.
- Some celestial bodies do not have their own heat and light. They are lit by the light of the stars. Such bodies are called Planets.
- The moon is the satellite of the earth and it moves round it.
| PLANET | REVOLUTION | ROTATION | SATELITE |
| Mercury | 88 days | 59 days | |
| Venus | 255 days | 243 days | |
| Earth | 365 days | 1 day | 1 |
| Mars | 687 days | 1 day | 2 |
| Jupiter | 11 years 11 months | 9 hours 56 minutes | 16 |
| Saturn | 29 years 5 months | 10 hours 40 minutes | 18 |
| Uranus | 84 years | 17 hours 14 minutes | 17 |
| Neptune | 164 years | 16 hours 7 minutes | 8 |
- Earth is 5th largest planet.
- Earth’s 2/3rd surface are covered with water.
- Earth is also known as blue planet.
- Diameter of the moon is 1/4th of the earth.
- Moon is 384400 km away from earth.
- Moon moves around the earth in 27 days. It takes exactly the same time to complete one spin. As a result, only one side of the moon is visible to us on the earth.
- Asteroids are the number of tiny bodies which also moves around the sun. They are found between the orbits of mars and Jupiter.
- The small piece of rocks which moves around the sun is called meteoroids.
- A galaxy is a huge system of billions of stars, and clouds of dust and gases.
- Universe is the collection of millions of galaxies.
- Venus is considered as Earth’s twin because its size and shape are very much similar to that of the earth.