GEOGRAPHY
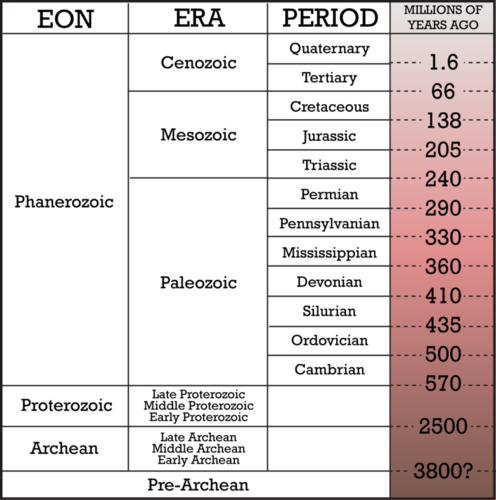
GEOLOGICAL TIME SCALE OF THE EARTH:
- The geological time scale (GTS) is a system of chronological measurement that describes the timing and relationships between events that have occurred throughout Earth’s history.
- Scientists developed the time scale by studying rock layers and fossils worldwide. Radioactive dating helped determine the absolute divisions in the time scale.
DIVISIONS OF GEOLOGIC TIME:
Proterozoic:
- No life possible as the Earth initially forms 4.6 billion years ago.
- Simple, single-celled forms of life appear 3.8 billion years ago, Land masses gather to make up a continent called “Rodinia”
Cambrian:
- Explosion of life.
- All existing phyla come into being at this time.
- Life forms in warm seas as oxygen levels rise enough to support life.
- Dominant animals: Marine Invertebrates (an animal lacking a backbone).
- Supercontinent Gondwana forms near the South Pole.
Ordovician:
- The 1st animals with bones appear, though dominant animals are still trilobites, brachiopods and corals.
- Four main continents: Gondwana, Baltica, Siberia and Laurentia.
Silurian:
- First land plants appear and land animals follow.
- Laurentia collides with Baltica and closes Iapetus Sea.
Devonian (Age of the Fish):
- Pre-Pangaea forms.
- Dominant animal: Fish.
- Present-day Arctic Canada was at the equator and hardwoods began to grow.
- Amphibians, evergreens and ferns appear.
Mississippian
- First seed plants appear.
Pennsylvanian
- Modern North America begins to form.
- Lizards and winged insects first appear.
Permian
- Pangaea forms.
- Reptiles spread across continents.
- The Appalachians Mountains rise.
- 90% of Earth’s species become extinct due to volcanism in Siberia.
Triassic
- First dinosaurs appeared.
- First mammals– small rodents appear.
- Rocky Mountains form.
- First turtle fossil from this period.
- Pangaea breaks apart.
Jurassic
- Pangaea still breaking apart.
- Dinosaurs flourish “Golden age of dinosaurs”.
- First birds appears.
- North America continues to rotate away from Africa.
Cretaceous
- First snakes and primates appear.
- Deciduous Trees and Grasses common.
- First flowering plants.
- Mass extinction.
Tertiary
- First horses appear and tropical plants dominate (Paleocene).
- Grasses spread and whales, rhinos, elephants and other large mammals develop.
- Dogs, cats, and apes appear (Oligocene).
Quaternary
- Modern humans develop and ice sheets are predominant- Ice age (Pleistocene).
- Holocene Humans flourish (Holocene).
RODINIA:
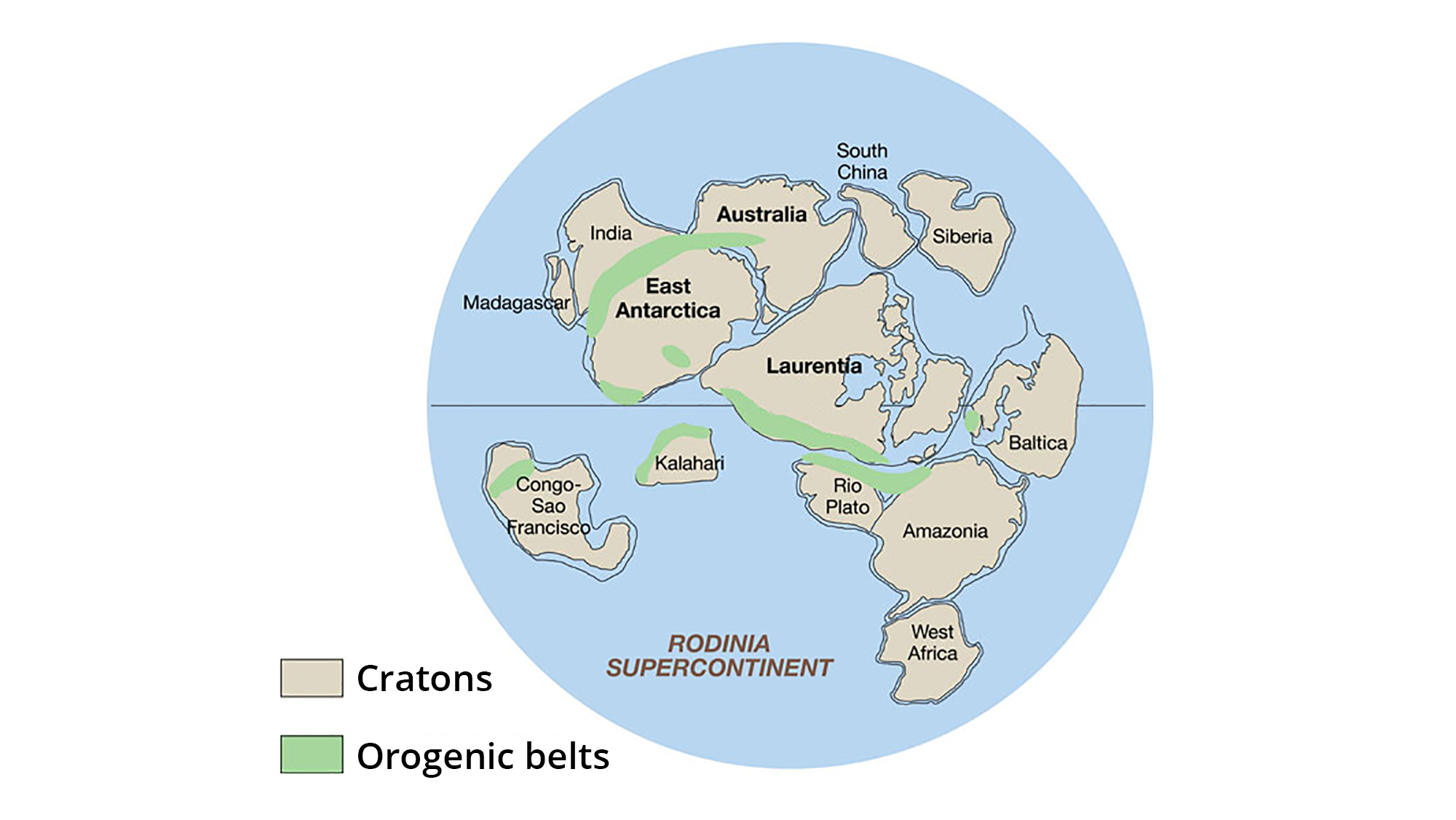
- Rodinia was a supercontinent that existed during the Neo-Proterozoic era and was named as it was thought to have been the original supercontinent that present day continents formed from.
- Its amalgamation began just after 1100 Million years ago, with the collision of Baltica (north-east Europe) and Amazonia (north-east South America) along the east coast of Laurentia (North America), Australia-Antarctica, the Kalahari (South Africa) and the Congo (Central Africa) cratons colliding along the west, south-west and south margins respectively and Siberia (eastern Russia) colliding with the northern margin.
- Due to its central position in the supercontinent, Laurentia is considered the heart of Rodinia.
- In Paleozoic era, breakup of Rodinia occurs around 750 million years ago and it resulted in all of these continents rifting off it and reforming into Gondwana (from 650-520 Million years ago, including South America, Africa, Australia, India and Antarctica) or Eurasia (North America and Baltica).
PANGAEA:
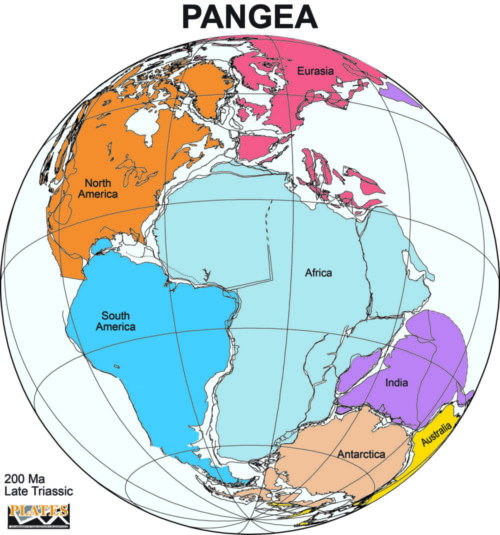
- During the mid-Mesozoic era, landmasses merged together and formed a continent known as Pangaea (which means all Earth).
- Pangaea was surrounded mega ocean called PANTHALASSA (which means all water). Panthalassa was the ancestor of today’s Pacific Ocean.
- Around 200 million years ago, the Pangaea began to split. Pangaea broke into two large continental masses as EURASIA and GONDWANALAND forming the northern and southern components respectively.
- India was the part of Gondwanaland.
- The northern supercontinent of Eurasia consisted of North America and most of Europe.
- The southern supercontinent of Gondwana (also called Gondwanaland) was the Palaeozoic amalgamation of South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia, and the Indo-Pakistani subcontinent, as well as several smaller terranes.
- The Atlantic Ocean did not exist even in ancestral form, because of the fusions of North America to Europe and of South America to Africa.
- Panthalassa was the ancestor of today’s Pacific Ocean.
- An arm of Panthalassa formed a deep east–west embayment in the eastern edge of Pangaea. This was the Tethys Sea. Tethys was the ancestor of the present Mediterranean Sea.
BREAKUP OF GONDWANALAND:
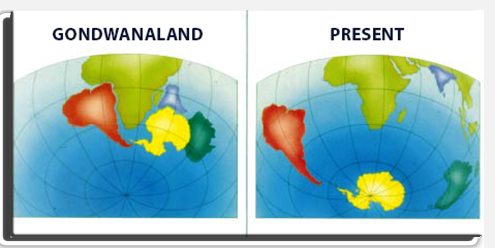
- During Gondwana’s stint as the southerly supercontinent, the planet was much warmer than it was today — there was no Antarctic ice sheet, and dinosaurs still roamed the Earth. By this time, it was the Jurassic Period, and much of Gondwana was covered with lush rainforest.
- The great supercontinent was still under strain, however. Between about 170 million and 180 million years ago, Gondwana began its own split, with Africa and South America breaking apart from the other half of Gondwana. About 140 million years ago, South America and Africa split, opening up the South Atlantic Ocean between them. Meanwhile, on the eastern half of the once-supercontinent, Madagascar made a break from India and both moved away from Australia and Antarctica.
- Australia and Antarctica clung together longer; in fact, Antarctica and Australia didn’t make their final split until about 45 million years ago. At that point, Antarctica started to freeze over as Earth’s climate cooled, while Australia drifted northward. (Today, the Australian continent still moves north at a rate of about 1.2 inches (3 centimeters) a year.
MOVEMENT OF INDIA:
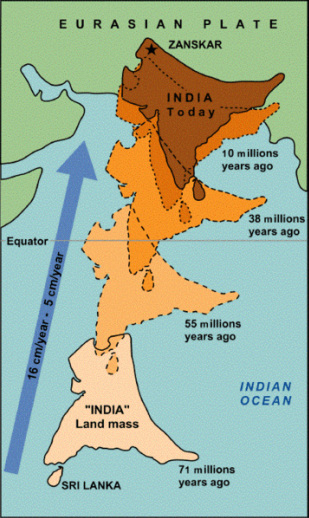
- India was the part of the supercontinent called Gondwanaland some 140 million years ago.
- When this supercontinent split up, a tectonic plate composed of India and modern Madagascar started to drift away.
- Then, India split from Madagascar and drifted north-eastward with a velocity of about 20 cm/year.
- India collided with Eurasia, a process that began 50 million years ago and continues to this day. This collision formed the Himalayas.
- Nowadays, India is still moving in the same direction but with a lower velocity of about 4 cm/year, due to the resistance of the Eurasian plate.
CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY:

- This theory was proposed by famous German geographer, Professor Alfred Wagner in 1924.
- According to this theory, before 200 million years ago, there was a single land mass surrounded by water which was named as Pangaea.
- About 200 million years ago, Pangaea got cracked into two parts i.e. (a) Eurasia and (b) Gondwanaland, and ocean water (Panthalassa) filled in it. As a result a narrow sea was created, known as Tethys’s sea.
EURASIA AND GONDWANALAND
Eurasia:
Eurasia is the combined landmass of Europe and Asia, forming the largest and most continuous continental area on Earth. It spans from the Atlantic Ocean (west) to the Pacific Ocean (east) and from the Arctic Ocean (north) to the Indian Ocean (south).
Gondwanaland:
Gondwanaland (or Gondwana) was a supercontinent that existed from the late Precambrian to the Jurassic period before breaking apart into the modern continents of the Southern Hemisphere. It included present-day South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia, and the Indian subcontinent.
After that, about 400 million years ago, Indian plate started drifting towards North East direction where it collided with Eurasian plate and as a result of collision, folding occurs over Tethys’s sea which resulted into upliftment of Himalayas and the process of upliftment is still going on.
EVIDENCE IN SUPPORT OF THE CONTINENTAL DRIFT
- Matching of continents (jig-saw-fit):
The shorelines of Africa and south America facing each other have a remarkable and unmistakable match.
- Rocks of same age across the oceans:
The belt of ancient rocks of 2000 million years from brazil coast matches with those of western Africa. The earliest marine deposits along the coastline of South America and Africa are of the Jurassic age. This suggests that the ocean did not exist prior to that time.
- Tillite:
It is the sedimentary rock formed out of deposit of glaciers. The Gondawana system of sediments from India is known to have its counter parts in six different landmasses of the Southern Hemisphere. At the base the system has thick tillite indicating extensive and prolonged glaciation. Counter parts of this are found in Africa, Falkland Island, Madagascar, Antarctica and Australia besides India. Overall resemblance of the Gondawana type sediments clearly demonstrates that these landmasses had remarkably similar histories.
- Placer deposit:
A placer is any waterborne deposit of sand or gravel that contains concentrated grains of valuable minerals.
The occurrence of rich placer deposits of gold in the Ghana coast and the absolute absence of source rock in the region is an amazing fact. The gold bearing veins are in Brazil and it is obvious that the gold deposits of Ghana are derived from Brazil plateau when the two continents lay side by side.
- Distribution of fossils:
The observations that Lemurs occur in India, Madagascar and Africa led some to consider a contiguous landmass “Lemuria” linking these three landmasses.
Mesosaurus was a small reptile adapted to shallow brackish water. The skeletons of these are found only in South Africa and Brazil. The two localities presently are 4,800 km apart with an ocean in between them.
SUMMARY:
- Super continent – Pangaea
- Ocean – Panthalassa
- Continent – SIAL rocks
- Ocean – SIMA rocks
- Mid- Mesozoic Pangaea broke up and drifted apart
LIMITATION OF CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY:
- Wegener failed to explain why the drift began only in Mesozoic era and not before.
- The theory doesn’t consider oceans.
- Proofs heavily depend on assumptions that are generalistic.
- Forces like buoyancy, tidal currents and gravity are too weak to be able to move continents.
- Gravitational pull of sun and moon.
- Idea of SIAL and SIMA.
- Modern theories (Plate Tectonics) accept the existence of Pangaea and related landmasses but give a very different explanation to the causes of drift.