OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
MATERIAL RESOURCE PLANNING (MRP):
- MRP is a systematic planning and control methodology for production and inventory.
- It is a procedure for planning and controlling the raw material, purchased parts and work in progress (WIP) inventories required in manufacturing.
- MRP is designed to answer three questions
- What is needed?
- How much is needed?
- When is it needed?
- It utilizes the product structure, processing information like production/procurement lead times and inventory status in a bid to produce the best plan.
- Thus MRP is a system of planning and scheduling the time phased material requirement for production operations.
OBJECTIVES:
- Inventory Reduction.
- Reduction in Production and Delivery Lead Times.
- Increased Efficiencies.
- Faster response to market changes.
- Improved labor and equipment utilization.
- Better inventory planning and scheduling.
- Reduced inventory levels without reduced customer service.
MRP SYSTEM:
The major advantage of MRP approach is its ability to plan discrete parts production for a very complex production system by scheduling all the activities required to meet the given master schedule while holding down work in progress inventory.
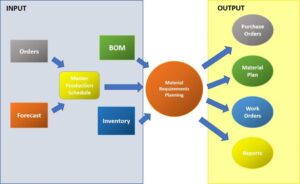
The major inputs to the system are:
- The master production schedule specifying what to produce and when.
- The product structure data including bill of material, routing files with manufacturing/ procurement lead time.
- The inventory status file for raw material, work in progress and finished goods.
Among the outputs from the package, the “gross and net requirement report” indicates the timing of order releases required to meet the master schedule.
The Capacity vs Load report determines whether resources required by the work centers are available to produce these orders which is useful in planning overtime.
The shop floor planning report is a listing of jobs by due date where the due date indicates when machining at that department should be completed in order to meet the schedule indicated by the gross and net requirement report. The shop floor supervisor will then release jobs to machines with completion time in hours and due dates for the items.
A typical commercial system provides additional information in the form of exception report indicating jobs to be expedited or de-expedited as a consequence of delays in production of components. De-expediting holds down work in process inventory.
MANUFACTURING RESOURCE PLANNING II (MRP II):
- Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II) is defined as a method for the effective planning of all resources of a manufacturing company. Ideally, it addresses operating planning in units, financial planning and has a simulation capability to answer “what-if” questions and extension of closed-loop MRP.
- It is an integrated information system used to plan and control inventories and capacities in manufacturing companies. MRP II system coordinates sales, purchasing, manufacturing, finance and engineering by adopting a focal production plan and by using one unified database to plan and update the activities in all the systems.

BENEFITS:
- For Manufacturing Functions:
- Better control of inventories.
- Improved scheduling.
- Production relationship with supplies.
- For Financial and Costing Functions:
- Reduced working capital for inventory.
- Improved cash flow through quicker deliveries.
- Accurate inventory records.
- Timely and valid cost and profitability information.
- For Design/Engineering Functions:
- Improved design control.
- Better quality and quality control.
ENTERPRISE RESOURCE PLANNING (ERP):
ERP is an extension of Material Requirement Planning and Manufacturing Resource Planning. ERP is an IT technique to provide the capabilities of collection, generation and storage of vast quantities of data to, an enterprise to automate business functions such as design, manufacture, distribution, service and recycling of product services and enable tracking of information throughout the company whenever required.
RELATED VIDEOS:
