EXPERIMENT
OBJECTIVE:
To conduct a tensile test on a mild steel specimen and determine the following:
- Limit of proportionality
- Elastic limit
- Yield strength
- Ultimate strength
- Young’s modulus of elasticity
- Percentage elongation
- Percentage reduction in area.
APPARATUS REQUIRED:
- Universal Testing Machine (UTM)
- Mild steel specimens
- Graph paper
- Scale
- Vernier Caliper
- Dividers
- Rulers
THEORY:
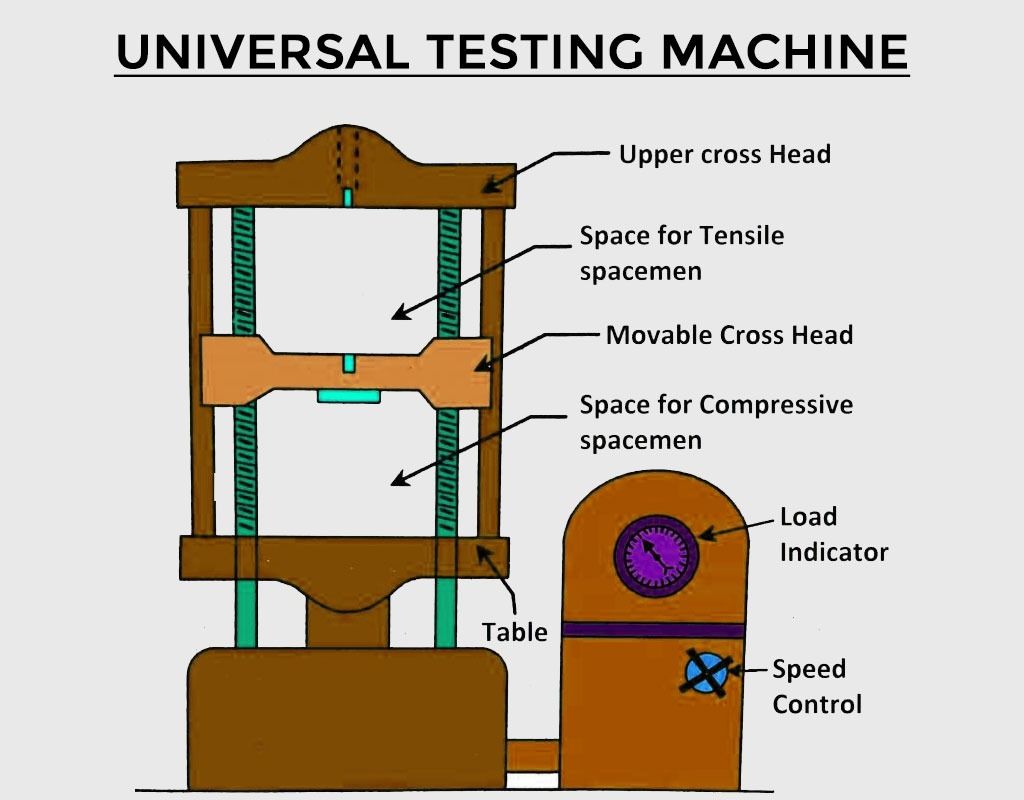
The tensile test is most applied one, of all mechanical tests. In this test ends of test piece are fixed into grips connected to a straining device and to a load measuring device.
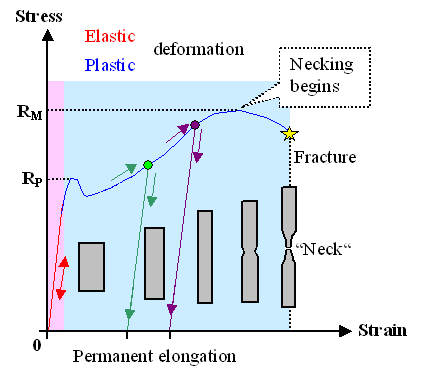
If the applied load is small enough, the deformation of any solid body is entirely elastic. An elastically deformed solid will return to its original form as soon as load is removed. However, if the load is too large, the material can be deformed permanently. The initial part of the tension curve which is recoverable immediately after unloading is termed as ELASTIC and the rest of the curve which represents the manner in which solid undergoes plastic deformation is termed PLASTIC. The stress below which the deformations essentially entirely elastic is known as the YIELD STRENGTH of material. In some material the onset of plastic deformation is denoted by a sudden drop in load indicating both an upper and a lower yield point. However, some materials do not exhibit a sharp yield point.
During plastic deformation, at larger extensions strain hardening cannot compensate for the decrease in section and thus the load passes through a maximum and then begins to decrease. This stage the “ULTIMATE STRENGTH”’ which is defined as the ratio of the load on the specimen to original cross-sectional area, reaches a maximum value. Further loading will eventually cause ‘neck’ formation and RUPTURE.
Usually a tension test is conducted at room temperature and the tensile load is applied slowly. During this test either round or flat specimens may be used. The round specimens may have smooth, shouldered or threaded ends. The load on the specimen is applied mechanically or hydraulically depending on the type of testing machine.
PROCEDURE:
- Measure the original length and diameter of the specimen. The length may either be length of gauge section which is marked on the specimen with a preset punch or the total length of the specimen.
- Insert the specimen into grips of the test machine and attach strain-measuring device to it.
- Begin the load application and record load versus elongation data.
- Take readings more frequently as yield point is approached.
- Measure elongation values with the help of dividers and a ruler.
- Continue the test till Fracture occurs.
- By joining the two broken halves of the specimen together, measure the final length and diameter of specimen.
OBSERVATIONS:
Record the following data:
- Initial diameter of specimen, d1 =
- Initial gauge length of specimen, L1 =
- Initial cross-section area of specimen, A1 =
- Load of yield point, Py =
- Ultimate load after specimen breaking, P =
- Final length after specimen breaking, L2 =
- Diameter of specimen at breaking place, d2 =
- Cross section area at breaking place, A2 =
OBSERVATION TABLE:
|
S. No. |
LOAD (N) |
EXTENSION (mm) |
ORIGINAL GAUGE LENGTH | STRESS = [frac up=”LOAD” down=”AREA”] [frac up=”N” down=”mm2“] |
STRAIN = [frac up=”INCREASE IN LENGTH” down=”ORIGINAL LENGTH”] |
| 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. |
CALCULATION:
- Limit of Proportionality = [frac up=”Load at limit of proportionality” down=”Original area of cross-section”] = …..[frac up=”N” down=”mm2“]
- Elastic Limit = [frac up=”Load at elastic limit” down=”Original area of cross-section”] = …..[frac up=”N” down=”mm2“]
- Yield Strength = [frac up=”Yield Load” down=”Original area of cross-section”] = …..[frac up=”N” down=”mm2“]
- Ultimate Strength = [frac up=”Maximum tensile load” down=”Original area of cross-section”] = …..[frac up=”N” down=”mm2“]
- Young’s Modulus = [frac up=”Stress below proportionality limit” down=”Corresponding strain”] = …..[frac up=”N” down=”mm2“]
- Percentage Elongation = [frac up=”Final length at fracture – Original length” down=”Original length”] = ….%
- Percentage reduction in area = [frac up=”Original area – Area at fracture” down=”Original area”] = ….%
PRECAUTIONS:
- The specimen should be prepared in proper dimensions.
- The specimen should be properly to get between the jaws.
- Take reading carefully.
- After breaking specimen stop to machine.
RESULT:
- Average Breaking Stress =
- Ultimate Stress =
- Average % Elongation =
RELATED VIDEOS FOR TENSILE TEST: