OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
Manufacturing System is a collection of integrated equipment’s and human resources whose function is to perform one or more processing and/or assembly operations on a raw material, parts or set of parts.
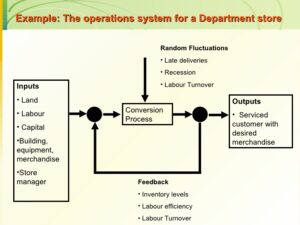
SYSTEM:
- A system may be defined as a purposeful collection of people, objects and procedures for operating within an environment.
- The features of a system are that these have inputs and outputs. The basic process of the system converts the resources inputs into some useful form of outputs.
TYPES OF MANUFACTURING SYSTEM:
Manufacturing systems varies from factory to factory and product to product. However, the most important issue is production volume. Most common ty of manufacturing systems are:
- Job Shop Production
- Batch Production
- Mass Production
-
JOB SHOP PRODUCTION
It is characterized by the low production volume. It has the following characteristics:
- Commonly used to meet a particular customer need.
- Production lot size is generally small.
- Product variety is very high.
- Production equipment are general purpose and flexible to meet specific customer need.
- Highly skilled labor is needed to handle the equipment as variety and product range are high.
MERITS
- It involves small investment in machinery and equipment.
- It is flexible and can be adapted easily to changes in product design.
- A fault in one operation does not result into complete stoppage of the entire process.
DEMERITS
- Raw materials and work in progress inventories are high due to uneven and irregular flow of work. Therefore, large storage space is required and material handling cost are high.
- Speed of work is slow and units costs are high.
- Complex schedule of activities is required to ensure smooth flow of work without any bottlenecks.
Job shop production is applicable where custom-made products are to be produced on a small scale. e.g., Ship, metro etc.
-
BATCH PRODUCTION
It is defined as the manufacture of a product in small or large batches or lots at intervals by a series of operations, each operation being carried out on the whole batch before any subsequent operation is performed.
- Suited of medium volume lot of same variety.
- Moderate product variety.
- Production equipment are general purpose but suitable for higher production volume.
- Jigs and Fixtures are used to reduce set up time and increase the production rate.
- Skill of labors is high but less as compared to job shop production.
- Machines and equipment arranged according to the sequence of operations.
- A particular operation on a batch is performed by one group and then it is passed for subsequent operations.
MERITS
- Products can be produced in mass quantities, reducing the overall cost per unit.
- Companies only focus on a small group of products, leading to greater quality control and product expertise.
- Cost of labor is reduced, as workers only focus on a particular task or set of tasks.
- Cost of machinery is reduced, as one machine can handle several different product configurations.
- Lends itself to repeat orders, meaning a smoother, more consistent production flow over time.
- Capital investment is low.
- It combines the features of both flow production and job production.
DEMERITS
- Work in progress inventory is high so large space is required.
- Due to frequent change in product design no standard sequence of operations can be used.
- Machine setups and tooling arrangements have to be changed frequently.
- Idle time between operations is more.
Batch production is applied when either the volume of output increase resulting in some repetitiveness or the market demand is not uniform throughout the year.
-
MASS PRODUCTION
Mass production refer to the manufacture of standardized parts or components on a large scale. Standardization of materials, machine, products and processes is the basic feature of mass production. The parts manufactured under mass production are combined in assembly line for making different products. Generally the degree of mechanization and automation is high.
- Suited for continuous identical parts.
- Suited for high demand items.
- Production lot size is very high.
- Production rate is continuous.
- Product rate is continuous.
- Product variety is low.
- Special purpose tools and equipment may be needed.
- Skill level of workers is low.
- High investment in machinery is needed due to specialized machines and special purpose operations.
MERITS
- It is usually ‘automated’ to the highest extent possible.
- Fewer labor costs.
- Faster rate of production.
- Capital and energy are increased while total expenditure per unit of product is decreased.
- Faster rate of production.
DEMERITS
- Machinery is very expensive to buy, so production lines are very expensive to set up.
- Workers are not very motivated, since their work is very repetitive.
- Not very flexible, as a production line is difficult to adapt.
- If one part of the line breaks, the whole production process will have to stop until it is repaired.
RELATED VIDEOS FOR TYPES OF MANUFACTURING SYSTEM:
For More Information- CLICK HERE
